Food Processing and related industries in India
Food processing and related industries in India - scope and significance, location, upstream and downstream requirements, supply chain management. The sector of food processing industry in India has grown rapidly and that has gained immense importance in modern time. Several academicians stated that food processing is the alteration of raw ingredients into food, or of food into other forms that is food processing may signify direct manufacturing of food or value addition on existing food. Food processing usually takes reaped crops or slaughtered animal products and uses these to yield long shelf-life food products. Food processing is done since ancient time when crude processing amalgamated slaughtering, fermenting, sun drying, preserving with salt etc. Currently, food processing adopts newest technologies and practices. There is easy availability of raw materials, changing lifestyles and relaxation in policies that has given a substantial momentum to the industry's development. This sector serves as a dynamic link between the agriculture and industrial segments of the economy. It is necessary to strengthen this link is to improve the value of agricultural produce; make sure remunerative prices to farmers and create favourable demand for Indian agricultural products in the global market. A push to the food processing sector indicates noteworthy development of the agriculture sector and ensures value addition to it.
Processes in a food processing industry:
There are two types of processes in a food processing industry:
- Manufacturing: Raw materials - Food.
- Value Addition: Increase shelf life and value of a manufactured food.
Significance of Food Processing Industries
In India, there is huge land for food production. It is estimated that more than 50% of Indian population work in Agriculture related actions. If there are good food processing industries in India, raw materials such as grains or meat can be converted into food for domestic and foreign consumption. Food processing units acts as a linkage between agriculture and industries. Food processing industries can absorb a major share of workers from the agriculture sector, who face disguised unemployment. It can result in better productivity and GDP growth. Reports indicated that Food processing averts food wastage and help in attaining food security. Processed food requires less space for storage. Processed food can be exported. This may assist government to get foreign exchange reserves.
The Indian food processing industry has remarkable capability to grow, considering the still promising levels of processing currently. Though India's agricultural production base is practically strong, wastage of agricultural produce is large.
Ministry of Food Processing Industries
The Ministry was established in 1998 and the industry segments that come under its purview are as under:Fruit & Vegetable processing (including freezing and dehydration)
Grain Processing
Processing of Fish (including canning and freezing)
Processing and refrigeration of certain agricultural products, dairy products, poultry and eggs, meat and meat products
Industries related to bread, oilseeds, meals (edible), breakfast foods, biscuits, confectionery, malt extract, protein isolate, high protein food, weaning food and extruded food products (including other ready-to-eat foods)
Beer, including non-alcoholic beer
Alcoholic drinks from non-molasses base
Aerated water and soft drinks
Specialised packaging for food processing industries.
Reasons for food processing: Foods are processed for five major reasons:
- Preservation for later consumption or sale to fetch better price
- Removal of inedible portions
- Destruction or removal of harmful substances
- Conversion to forms desired by the consumer and
- Subdivision into food ingredients.
Scope and Significance of Food Processing Industries in India
According to news reports, Food processing is any activity that changes the raw food stuff or semi-finished food into a suitable form for the use of shopper. The food processing industry has grown considerably in the last few decades India. The increase in the incomes of the working class has led to increase in the disposable income to be spent on processed foods. The change in the food habits of the working class who prefer readily available convenient foods is another important factor. India is considered as one of the top producers of fruits and vegetables and other food stuff. Henceforth availability of raw material makes it favourable for the development of this sector.
India has good status in producing numerous food products like milk, ginger, banana, guava, papaya, and mango. It has second rank in the production of rice, wheat, potato, sugarcane, cashew nut, tea. India is among the top 5 countries in producing coffee, tobacco, spices, and seeds. With such a huge raw material base, it can be assessed that India become the leading supplier of food items around the globe. News reports indicated that there are more than 30 companies listed in BSE/NSE in food processing sector. However, the major companies are Dabur India, Gitz, Godrej industries, Haldiram, MTR foods, Parle agro, HUL, Britannia Industries, ITC, Nestle, Pepsi and Cadbury India. There is still a lot of scope for products related to meat, poultry; fisheries, milk products, beverages, grain processing.
Section wise assessment of food processing Industries in India:
I. Dairy Sector: India holds first rank in the world in terms of milk production. Milk and milk products contribute to a significant 17 per cent of the country's total expenditure on food. Traditional dairy products account for about 50 per cent of the total milk produced.
II. Fruits and Vegetables: India produces huge amount of fruits and vegetables in the world. It is the second largest vegetable and third largest fruit producer accounting for 8.4 per cent of the world's food and vegetable production. Major products exported include fruit pulps, pickles, chutneys, canned foods, concentrated pulps and juices and vegetables.
III. Grain Processing: India has third position in the production of grains in the world.As per the estimates, India produced nearly 209.32 million tonnes of grains in 2005-06. India's production covers all major grains: rice, wheat, maize, barley and millets like jowar, bajra and ragi.
IV. Meat and Poultry Processing: India has huge number of livestock population in the world accounting for 50 per cent of buffaloes and 16 per cent of the goat population. Animals generally used for production of meat are cattle, buffaloes, sheep, pigs and poultry.
V. Fisheries: India has third position in producing fish in the world and second in in-land fish production in the world. The Fisheries sector in India has been classified into marine, inland and aquaculture. Processed fish product exports comprises of conventional block frozen products, individual quick frozen products and minced fish products like fish sausage, cakes, cutlets, pastes.
VI. Consumer Foods Including Packaged foods, Beverages and Packaged Drinking Water
Packaged Foods: It is estimated that Packaged food segments in India registered a growth of 8 per cent in 2005-06. Soup market is small in India.
Beverages: The beverages market in India mainly include non-alcoholic beverages which can be broadly classified into carbonated drinks, non-carbonated drinks and hot beverages. Hot beverages include health drinks such as white beverages such as Horlicks and brown beverages such as tea/coffee as well as branded drinks for example, Boost. India is the largest producer of tea in the world.
Staples- Bread, Wheat Flour, Salt and Sugar: Bread is gradually entering to be a staple product consumed by people of all economic classes in India. It is estimated that India is the second largest producer of wheat in the world with an output of more than 70 million tonnes.
It has been appraised by experts that the total food production in India is expected to double in the coming years and there is an opportunity for huge investments in food and food processing technologies, skills and equipment, especially in fields of Canning, Dairy and Food Processing, Packaging, Frozen Food/Refrigeration and Thermo-Processing. Fruits and Vegetables Processing, Fisheries, Milk and Milk Products, Meat & Poultry, Packaged/Convenience Foods, Alcoholic Beverages & Soft Drinks and Grain processing are vital sub-sectors of the food processing manufacturing. The customer product groups like confectionery, chocolates and cocoa products, Soya-based products, mineral water, high protein foods, soft beverages, alcoholic and non-alcoholic fruit beverages, along with the health food and health food supplements is another fast growing division of this industry which is gaining huge popularity.
It is recorded that India produces nearly 16% of the world's total food grain manufacture. It is one of the largest producers of agricultural produce. India has a massive potential domestic demand for processed foods other than the demand from the exports. There are many socio-economic factors that are driving the demand side of the Indian Food Processing Industry. The varying consumption patterns, both in tier 1 and tier 2 cities, increasing income levels among the middle-class and changing lifestyles, are some of the factors providing the demand side drive for the Food Processing Industry. Furthermore, the central government has given a priority to all agro-processing industries.
Resource advantage of India: India is rich in natural resources. Different soil types and different climate types for farming of diverse food crops, long coastal line appropriate for fishing, huge resource of domestic animals.
The main advantage is that it increases employment. It is expected to create more than 10 lakh new jobs.
Curbing Migration: Agricultural resources in India provides employment in rural areas, hence reduces relocation from rural to urban and resolves issues of urbanization.
It also control food inflation: These resources removes issues of wastage or middle man. It curbs food inflation. Indirect relief on non-food inflation too.
Crop Diversification: Because of long shelf life, agriculturalists can expand their products.
Government initiatives to boost food processing: Various government initiatives such as attracting FDI, discount in excise duties have enhanced food processing.
Future driver of Indian growth: Food processing relates to around 10% of GDP in agriculture-manufacturing sector.
Location of food processing industries in India:
India has more than 35000 listed units. Most of the food processing factories are concentrated in the coastal states due to accessibility to marine food processing. Major coastal states includes: Andhra, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Kerala, Gujarat, Punjab and WB. Non-coastal states include UP, Punjab.Major Segments Of Food Processing: (Source: Ministry of food processing in India. 2014)
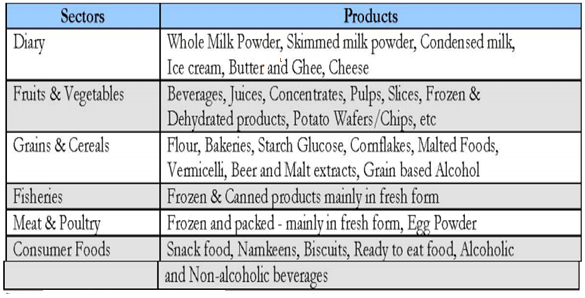
Upstream and Downstream Requirements Of Food Processing Industries
Upstream stage: The upstream stage of the production process includes searching for and extracting raw materials. The upstream part of the production process does not do anything with the material itself, such as processing the material. This part of the process simply finds and extracts the raw material. Therefore, any industry that relies on the extraction of raw materials commonly has an upstream stage in its production process.Upstream requirements:
Accessibility to raw materials.
Modern extraction techniques.
Good linkages with farmers.
Storage facilities for raw materials like Grains, Meat, Fish.
Quality testing facilities.
Transport facilities.
Work force
Downstream stage: The downstream stage in the production process involves processing the materials collected during the upstream stage into a ended product. The downstream stage further comprises of the genuine sale of that product to other businesses, governments or private individuals. Downstream process has direct contact with customers through the finished product.
Downstream requirements:
Latest processing techniques.
Latest processing machinery.
Quality testing facilities.
Organized retail stores for faster distribution.
Work force.
Supply Chain Management
Supply chain is a system that relates a corporation with its suppliers and clienteles. In Supply chain, Upstream-downstream depends on the point of reference. In Food Processing Industry, raw materials such as grains, raw meat, and fish are collected by different sources. These sources may do preliminary processing of these to make components of a food product before passing over them to the main manufacturer through many middle men. The producer does the final processing of these components to make the food product. This completes only the first stage of supply management. Now the finished product has to be delivered to the customer. In this process, there will be a number of middle men and stages. The manufacturer usually hands over the food product to a whole sale dealer. The wholesaler deliver the product to a retailer from where the consumer buys the processed food item for his personal use.Importance of Supply Chain Management in Food Processing Industry: Good Supply Chain Management practices in nation enhance economy as a whole. Good supply chain links helps farmers, manufactures, wholesalers, retailers and consumers.
Supply chain improvement and promotion
|
Backward linkage |
1. Regular supply of raw
material through contract farming. 2. Incentives in the form of
reimbursement |
|
Forward Integration |
1. Ensuring regular market for
their products by establishing linkages by market. 2. Assistance for market survey,
test marketing, brand building. |
|
Generic advertisement |
1. Marketing promotion campaign
for new products mix and brand name support. 2. Publications, journals, press
advertisements. |
|
Promotional activities |
1. Seminars, workshops,
symposiums. Studies, surveys, feasibility
reports to assess the potential and relevant aspects. 2. Association with APEDA,
CFTRI, Industry association etc. Participation in national and
international exhibitions and fairs. |
Hindrances in the Growth of Food Processing Industries
It has been observed that there are many factors that lead to the growth of food processing industries in India. In spite of huge development in this industry, there are several constraints that hinder the development of food processing industries. Major constraints is that this industry is capital intensive. It creates a strong entry barrier and allows lesser number of companies to enter the market. It means there is not tough competitions among industry players which can reduced efforts to improve the quality standards.Another hindrance is small size companies. Indian food processing companies are small and cannot compete with global players which invest heavily on R & D.
There is lack of good laboratories in India which impede the growth of food processing Industries in India. Food export to US and EU demands high quality standards. India lack good laboratories to check heavy metal and other toxic contamination in food.
Other limitations are as follows:
Lack of skilled work force. There are only a few graduates in Food Technology.
Lack of right vision and support from the government at the right time.
Lack of good transport facilities. Roads are overburdened.
Lack of storage facilities and good production techniques.
Lack of organised retail.
Limitations in supply chains.
Limitations in the quality.
Lack of modern guidelines
Government Initiatives for Development of Food Processing Industry in India:
Government of India took many initiative to improve the status of food processing industries. Government is motivating food processing industries through:100% FDI in this sector.
Agri Export Zones.
National Mission on Agriculture.
Major Schemes implemented by Government that include:
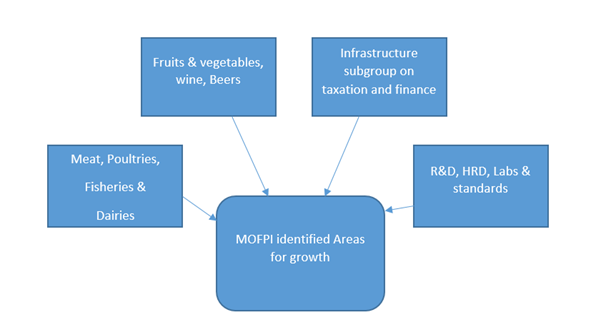
Vision 2015 for food processing: The Ministry of Food Processing Industries (FPI) has sponsored a study to propose a roadmap for the development of food processing sector. M/S Rabo Bank has conducted a study and submitted a Vision Document suggesting strategy and action plan for food processing sector in India such as Vision 2015. Vision Document suggested strategy to make sure speedy development of food processing Industries in India. The adopted Vision 2015 provides for enhancing the level of processing of perishable from 6% to 20%, enhancing value addition from 20% to 35% and increasing India's share in global food trade from 1.5% to 3% by the year 2015.
Various schemes under vision 2015
National Mission on food processing: Ministry of Food Processing Industries (MOFPI) implemented a new Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS) National Mission on Food Processing (NMFP) on 1st April 2012 for implementation through States/UTs. The NMFP visualises establishment of a National Mission as well as corresponding Missions in the State and District level. The major objectives of this schemes are as follows:
- To augment the capacity of food processors working to upscale their operations through capital infusion, technology transfer, skill up gradation and handholding support.
- To support established self-help groups working in food processing sector to facilitate them to achieve SME status.
- Capacity development and skill upgradation through institutional training to ensure sustainable employment opportunities to the people and also to reduce the gap in requirement and availability of skilled manpower in food processing sector.
- To raise the standards of food safety and hygiene to the globally accepted norms.
- To facilitate food processing industries to adopt HACCP and ISO certification norms
- To augment farm gate infrastructure, supply chain logistic, storage and processing capacity.
- To provide better support system to organized food processing sector
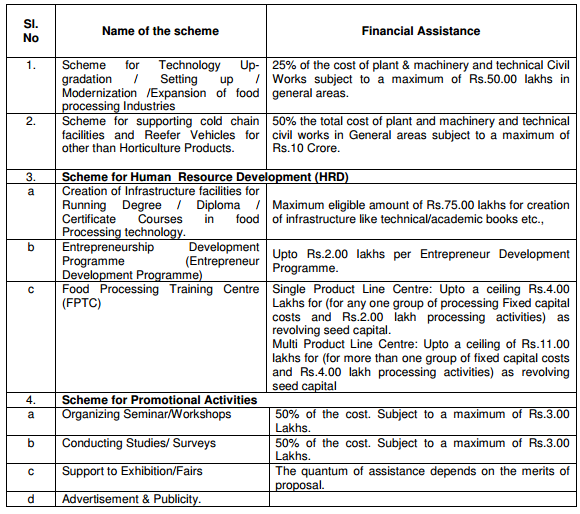
Major Programmes / Schemes to be covered under NMFP during 2012-13 are
Mega food parks: Mega Food Park Scheme is the effective program of the Ministry of Food Processing Industries, Government of India. Mega Food Park Scheme suggests a demand driven/pre-marketed model with strong backward/forward linkages and sustainable supply chain. It can be said that the policy of Mega Food Park is intended to offer a mechanism to relate agricultural production to the market through bringing together farmers, processors and retailers in order to maximize value addition, reduce wastages, increasing farmers' income and creating employment opportunities particularly in rural sector. The Mega Food Park Scheme is based on �Cluster� approach and visualizes a well-defined agri/ horticultural-processing zone containing state-of-the art processing facilities with support infrastructure and well-established supply chain.
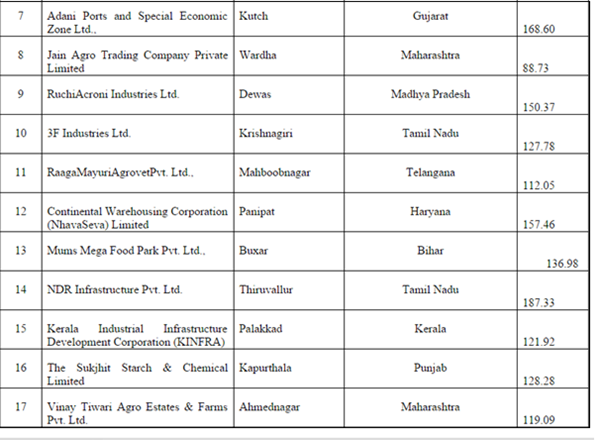
Total 42 Mega Food Parks have been sanctioned by the Government for setting-up in the country. This step of the Government will create huge modern infrastructure for food processing sector and provide impetus to the development of the area.
List of Mega Food Parks
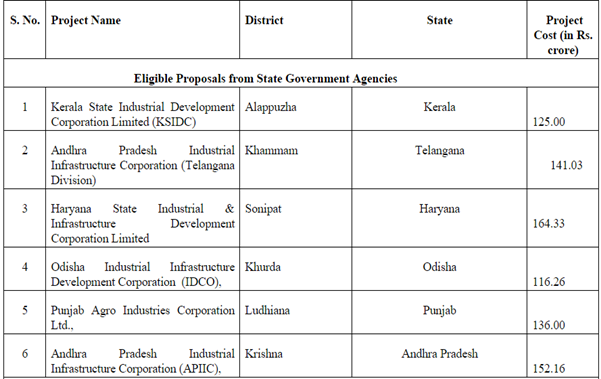
Eligible Proposals from Private Sector Agencies
Modernization of abattoirs: According to reports, The Scheme of Modernization of Abattoirs was launched during 2008. The Scheme is employed through local bodies (Municipal Corporations and Panchayats)/Public Sector Undertakings/Cooperatives/ Boards under Government and will have the flexibility for participation of private investors on PPP basis. The scheme offers facilities for scientific and less painful slaughtering, chilling, waste treatment plant, by-product utilization, water and power with required sanitary / phyto sanitary conditions for modernization of abattoirs. Transformation of abattoirs will also enhance essential supply base of hygienic raw material to the meat processing industry, both for domestic consumption and exports, besides discouraging illegal slaughtering. Scheme of Setting up/ Modernization of Abattoirs offers for initiation of private capital, better technology, backward and forward linkages. The system also provides for execution of projects preferably under PPP mode with the involvement of local bodies and has the flexibility for involvement of private investors/exporters on a BOO/BOT/JV basis.
Cold Chain Infrastructure: The Government of India identifies that development of cold chain is an essential step in upgrading India's food processing industry and consequently offers many incentives for promoting growth Scheme for Integrated Cold Chain, Value Addition and Preservation Infrastructure has major objective to motivate setting up of cold chain facilities to provide integrated cold chain and preservation infrastructure facilities without break from the farm gate to the customer.
Scheme of Technology Up-gradation/Establishment/ Modernization of Food Processing Industries: The Scheme is implemented to support prospective entrepreneurs to establish food processing units to decrease the wastage of agricultural and horticultural produce.
R&D, QA, Codex and Promotion:
Scheme for Quality Assurance, Codex, R&D and Other Promotional Activities is being executed to build infrastructure of food testing laboratories in the country to establish quality monitoring system for food processing, implement HACCP/ISO22000, ISO14000/GHP/GMP and other quality management systems and to encourage research and development for innovative products and process.
Food Testing Laboratories: The objective of the scheme is to guarantee safety and quality of food products with the analysis of the samples received from food processing industries and other stakeholders. The formation of a surveillance system to monitor the quality and composition of food and thereby ensuring compliance of international standards on food.
Implementation of HACCP: The goal of the scheme is to encourage the food processing industries to adopt food safety and quality assurance mechanisms such as total quality management including ISO 14000, ISO 22000 HACCP, GMP, GHP, to prepare them to face global competition in post STO Regime, to enable faithfulness to stringent quality and hygiene standards, to improve product acceptance by foreign buyers and to keep Indian industry technologically up-to-date of international best practices.
Research & Development: Main aim of this scheme is that the end product/findings of R&D work must benefit food processing industries in terms of product and process development, improved packaging, value addition and leading to advanced products and process with profitable value.
Promotional Activities: In the Scheme for Promotional Activities, the Ministry offers financial support for organizing pan India level Seminars/Workshops/Fair/ Exhibitions and also partake in pan India level Fair/Exhibitions spearheaded by Apex Industry Associations and Autonomous Bodies/PSUs of Govt. of India with the objective of distribution of information regarding food processing industries.
Scheme for Human Resource Development: Ministry of Food Processing Industries has executed the Scheme for Human Resource Development since 9th Plan and onwards to boost the supply of trained manpower/ personnel at all levels for food processing sector such as entrepreneurs, managers, sales persons, floor workers.
The ministry of food processing has taken the following initiatives for policy support for food processing Industries:
- Formulation of the National Food Processing Policy
- Complete de-licensing, excluding for alcoholic beverages
- Declared as priority sector for lending in 1999
- 100% FDI on automatic route
- Excise duty waived on fruits and vegetables processing from 2000 - 01
- Income tax holiday for fruits and vegetables processing from 2004 - 05
- Customs duty reduced on freezer van from 20% to 10% from 2005 - 06
- Implementation of Fruit Products Order
- Implementation of Meat Food Products Order
- Enactment of FSS Bill 2005
- Food Safety and Standards Bill, 2005
The Centre has requested state Governments to undertake the following improvements:
- Amendment to the APMC Act
- Lowering of VAT rates
- Declaring the industry as seasonal
- Integrate the promotional structure

