Capacity Planning
Capacity is defined as the ability to deliver in a definite period. Capacity refers to the skill to hold, receive, store, or accommodate. In general business logic, it's often analysed as the amount of output that a system is capable of achieving over specific period of time (Jacobs & Chase 2008,). It also denotes to the constraint which the operating element is able to process, the amount of services executed or tangible products produced. The essential elements and considerations needed to be taken into account before-hand are what type of capacity whether its equipment, space or human skills are needed, how much of it is required and the timeframe of when those factors are to be accessible (Beamer 2010). Capacity planning is the proficient use of resources by projecting production needs. It can be applied to company's computer network, storage, work force maintenance and product manufacturing, among other things. A small business should use capacity planning because of the financial and logistical benefits it offers. Basically the notion of Capacity planning indicates that it is the long-term strategic decision which establishes a company's capability to supply products or services. Capacity planning is typically undertaken using complicated computer software. Capacity planning outlines the personnel and equipment for small business need in order to maintain current operations and reach goals. That information becomes significant when developing yearly budgets and the spending portions of business and marketing plans. Management team can directly estimate how much expenses will be, it becomes easier to develop financial projections.
Capacity planning engages analysis and decisions to balance capacity at a production or service point with demand from customers (orders, visitors). This way, it is useful to consider of information flows and constraints in a client-server relationship. Operation managers should have enough production or service capacity (machines, space, staff skills and hours, stocks, vehicles) to supply the accurate quantity at the right time. Thus must optimise the use of resources. It can be said that capacity planning is the viewpoint of businesses to work out their capabilities. Therefore, capacity planning is the one of key performance elements of a functional business. When executed through careful and considerate calculations, capacity planning can be the single ingredient which generates the profits for an organization. However, companies which do not focus enough on management of strategic capacity planning may undergo serious difficulties or even terrible problems especially during a growth or starting period. According to Professors F. Robert Jacobs and Richard B. Chase (2008), strategic capacity planning as a method which determines the total levels of capacity for resources mentioned above. The common feature of these resources is the scarce and the finite nature, which is normally described as "capital-intensive" but also the availability in terms of often placed secondary in importance - time reflecting the reasons why planning is necessary.
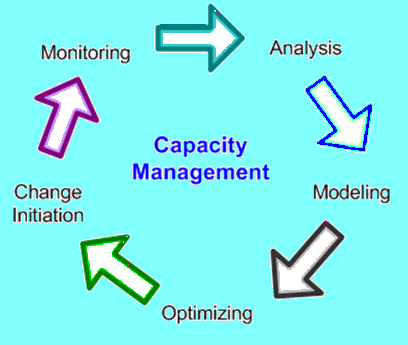
Figure: Capacity management
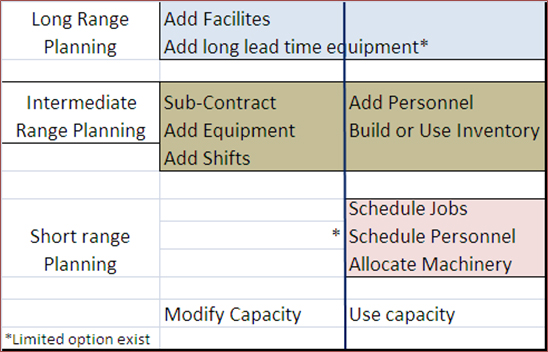
Capacity planning based on the timeline is categorized into three main groups such as long range, medium range and short range.
Long Term Capacity: Long range capacity of company is dependent on various other capacities like design capacity, production capacity, sustainable capacity and effective capacity. Design capacity is the maximum output possible as indicated by equipment manufacturer under ideal working condition. Production capacity is the utmost output possible from equipment under normal working condition or day. Sustainable capacity is the maximum production level achievable in realistic work condition and considering normal machine breakdown, maintenance, etc. effectual capacity is the best production level under pre-defined job and work-schedules, normal machine breakdown, maintenance, etc.
Medium Term Capacity: The tactical capacity planning performed by organization for 2 to 3 years of a time frame is called medium term capacity planning.
Short Term Capacity: The strategic planning done by organization for a daily weekly or quarterly time frame is referred to as short term capacity planning.
Figure: Types of capacity planning over a time frame
Main Purpose of Capacity Planning
Reason of Capacity planning is for an organization is to go with its supply competence and capability levels with the predicted demand by the purchaser. Capacity plan is formed to support the company's main competitive plan and it has to be in order and correlate with it. The exactness of the capacity plan is in sync with the company's ability to actualise their capabilities enabling them to have specific respond to the needs of the customer. Should the situation be so that the demand is too extreme, through a detailed plan it is easy to seek out the required steps which are to be done in order to satisfy the demand. Insufficient or otherwise inadequate capacity may turn out to be costly for the company as unpleased customers are lost and such a market attracts competition fasters. The demand and how it is predicted will be discussed further (Jacobs & Chase 2008).
There is a great significance of capacity planning such as it impacts ability to meet future demands, affects operating costs, major determinant of initial costs, involves long-term commitment, affects competitiveness and also impacts ease of management. Capacity planning is the primary step when company wants to launch produce more or a new product. Once capacity is assessed and a need for a new expanded facility is decided, facility location and process technology activities take place. Capacity planning is performed to estimate whether the demand is higher than capacity or lower than capacity. That is compare demand versus capacity. It assists company to recognize and plan the actions necessary to meet customer's present and future demand. Determinants of Effective Capacity/Output are Facilities, layout, Products or services, product mixes/setups, Processes, quality, Human considerations, motivation, Operations, scheduling and synchronization problems, Supply Chain factors, material shortages and External forces, regulations.
Capacity Measurement
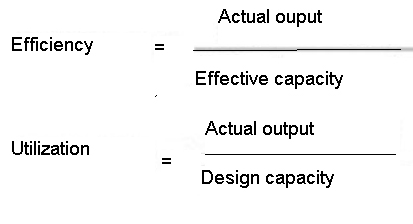
Capacity as an expression is intended at the rates of output of the operations in question. The output is usually indicated through a rate which presents the amount of deliverables completed in a period of time. The actual output rate gives an indication of the daily result. In order to assess the rate further to determine the actual efficacy, two capacity efficiency performance indicators are to be used (Jacobs & Chase 2008, 54). The successful capacity is a measure which the process was designed for, but which can be practically expected as a result; while taking into consideration diverse factors which keep the process reaching its peak due to their inevitability. Design capacity is the best level for an operation, process or a facility to deliver. In manufacturing, the design capacity reveals the volume of productivity with minimum cost of an average unit. Both of the ratios are usually shown in percentages and give an idea of improvement needs. Efficiency ratio demonstrates how effectual in terms of productivity whereas utilization ratio indicates the need for improvement within the process itself.
Figure: Capacity efficiency rate formula & Capacity utilization rate formula:
Strategies of Capacity Planning
The main category of capacity planning is lead strategy, lag strategy, match strategy, and adjustment strategy. Lead strategy is addition capacity in expectation of an increase in demand. Lead strategy is an aggressive scheme with the aim of attracting customers away from the company's competitors through enhancing the service level and reducing lead-time. It is also a strategy aimed at reducing stock out costs. A large capacity does not necessarily mean high inventory levels, but it can imply in higher cycle stock costs. Excess capacity can also be rented to other companies. Lag strategy is a more conservative strategy. It decreases the danger of waste, but it may result in the loss of possible customers either by stock-out or low service levels. Match strategy is adding capacity in small amounts in response to varying demand in the market. This is a more moderate strategy. Adjustment strategy is adding or reducing capacity in small or large amounts due to consumer's demand, or due to major changes to product or system architecture.
Method of capacity planning differs from company to company. A long-term outlook may cover months to years. An operations strategy is necessary that include overall organizational capacity (production sites, hotels, hospital wings (rooms and beds), warehouses, production lines/machinery, computer up-grades and investment in new facilities. Medium-term forecasting demand and scheduling available capacity to best meet or balance that demand. This typically involves manufacturing or requirements planning, machine scheduling, and materials requirements plan. Short-term day-to-day adjustments are typical of capacity management. Capacity planning gives an operational structure and makes certain to the management of supplies and scheduling of resources. There are fundamentally three essential steps for capacity planning.
- Determine Service Level Requirements: The first step in the capacity planning process is to classify the work done by systems and to quantify users' expectations for how that work gets done.
- Analyse Current Capacity: Second step is the current capacity of the system must be analysed to determine how it is meeting the needs of the users.
- Planning for the future: Third step is to use forecasts of future business activity and future system requirements are determined. Implementing the required changes in system configuration will guarantee that enough capacity will be available to uphold service levels, even as circumstances change in the future.
Issues in capacity planning: Capacity planning has huge significance because it gives financial benefits of the efficient use of capacity plans within material requirements planning systems and other information systems. Inadequate capacity can result in declining delivery performance, needlessly increase work-in-process, and aggravate sales employees and those in manufacturing. However, surplus capacity can be expensive and unnecessary. The incapability to correctly manage capacity can be obstacle to the attainment of maximum firm performance. It is observed that when there is a failure to recognize the crucial nature of managing capacity, it can lead to disorder and severe customer service problems. If there is a disparity between available and required capacity, adjustments should be made. Companies cannot have perfectly-balanced material and capacity plans that simply contain emergency orders. If flexibility is the firm's competitive priority, excess capacity would be suitable. Service capacity planning can present a number of challenges related to the inability to store services, the need to be near customer and the degree of demand volatility.
To summarize, Capacity planning is the procedure of assessing the production capacity needed by an organization to fulfil requirements for its products. Capacity is the rate of productive capability of a facility. Capacity is usually expressed as volume of output per time period. The aims of capacity planning are to identify and solve capacity problem in a timely manner to meet consumer needs, to maintain a balance between required capacity and available capacity, the goal of capacity planning is to minimize this discrepancy.

