Export Import procedures
Export, import procedure serve as important guide to international trade operations and contains a sample of virtually every relevant document used in foreign trade (Johnson, 2010).
Export
Export of goods take place when there is a change of proprietorship from a resident to a non-resident; this does not essentially infer that the goods in question physically crosses the border. However, in specific cases national accounts credit changes of ownership even though in legal terms no change of ownership takes place such as cross border financial leasing, cross border deliveries between affiliates of the same enterprise, goods crossing the border for significant processing to order or repair. Also smuggled goods must be included in the export measurement. Exporter has to submit ‘shipping bill’ for export by sea or air and ‘bill of export’ for export by road. Relevant documents i.e. copies of packing list, invoices, export contract, letter of credit are also to be succumbed.
For many companies, export begins in the sale or marketing department. That department may develop leads or identity clients located in other countries. Inquiries or orders may come from potential customers through company website where the destination is not identified. When such orders come in, sales person need to determine what steps are different from its domestic sale in order to fill those export orders?
Export: Order processing quotation (Source: Johnson, 2010)
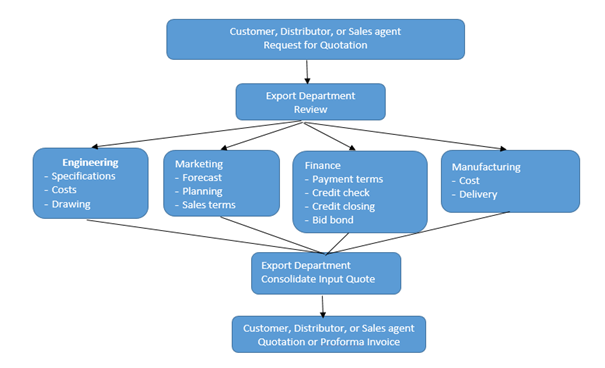
Because export orders require special procedures in manufacturing, credit checking, ensuring, packing, shipping and collection, it is likely that number of people within the company may have input on the appropriate way to fill the order. As the export increases, the handling of such orders should become more routine and the assignment of special procedures related to an export sale should be given to specific personnel (Johnson, 2010).
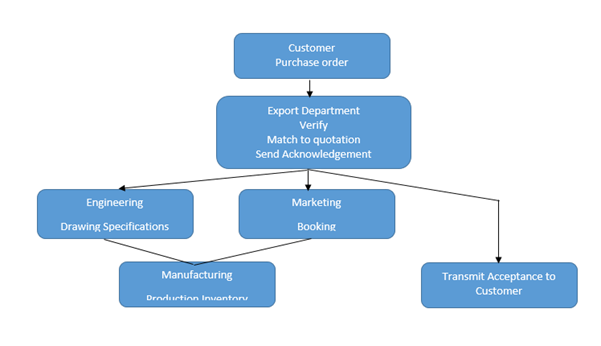
Export order processing: Order entry (Source: Johnson, 2010)
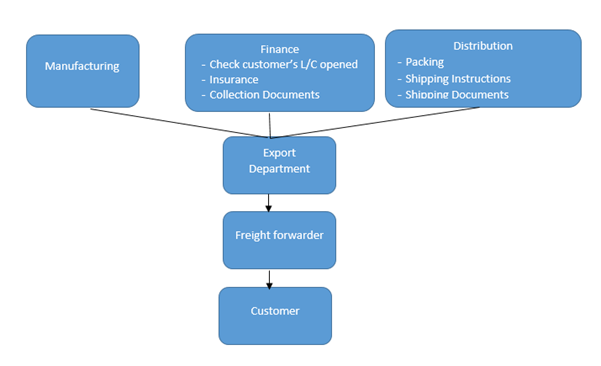
Export order processing: Shipment (Source: Johnson, 2010 )
Basic Export Procedures
- Market Research and Setting Objectives of Distribution: Selecting target markets, methods of exportation and channels, setting foreign market objectives on pricing and terms
- Trade Regulations:
- Export regulations and requirements
- Overseas import regulations and requirements
- Patent, trademark and copyright
- Making Contacts:
- Investigations from interested overseas buyers
- Checking buyer's background from ECIC and / or banks
- Quotation and Terms:
- Making offers and quotation for potential buyers
- Costs, quotations and pro forma invoices, and terms of sale
- Sales Contract:
- Confirming the sales contract and terms of transaction such as payment terms.
- Contract Execution:
- Producing or sourcing goods
- Packing and labelling
- Arranging shipment
- Preparing exports documentation
- Arranging insurance, if necessary
- Customs Clearance:
- Arranging export declaration and applying for export licence when necessary.
- Getting paid: - Subject to the payment terms specified in the sales contract, the exporter should present the required documents to the relevant parties for payment
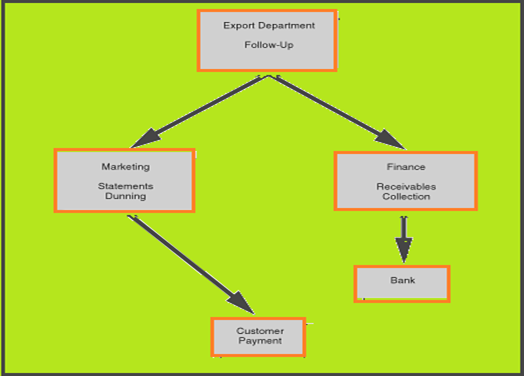
Export order processing: Collection (Source: Johnson, 2010)
Import
Import is explained as bringing products into own country from a place outside national border. It can be said that Import trade refers to the purchase of goods from a foreign country. The procedure for import trade varies from country to country depending upon the import policy, statutory requirements and customs policies of different countries. In almost all countries of the world import trade is controlled by the government. The aims of these controls are appropriate use of foreign exchange restrictions, protection of indigenous industries etc. The imports of goods have to follow a procedure.
A manufacturer's import department often grows out of the purchase department, whose personnel have been assigned the responsibility of procuring raw material or components for the manufacturing process. For importers or trading companies that deal in finished goods, the import department may begin as a result of being appointed as the distributor for a foreign manufacturer (Johnson, 2010).
In Indian context, the import and export of goods is ruled by the Foreign Trade (Development & Regulation) Act, 1992 and India’s Export Import (EXIM) Policy. India’s Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) is the major governing body and responsible for all issues associated with EXIM Policy. Importers are essential to register with the DGFT to obtain an Importer Exporter Code Number (IEC) issued against their Permanent Account Number (PAN), before engaging in EXIM activities. After an IEC has been obtained, the source of items for import must be identified and declared. The Indian Trade Classification – Harmonized System (ITC-HS) allows for the free import of most goods without a special import license.
Basic Import Procedures
- Setting Market Objectives:
- Setting market objectives on pricing and terms
- Sourcing Products:
- Identifying potential suppliers
- Sourcing channels of distribution
- Trade Regulations:
- Import regulations and requirements, and checking whether import licence is required
- Patent, trademark and copyright
- Making Contacts:
- Sending enquiries to suitable suppliers
- Settling Quotation and Terms:
- Analysing the supplier's quotation and offers
- Costs and terms of sale
- Financing the Purchase:
- Preparing for working capital
- Types of bank financing and application, such as exporter credit or other bank facilities
- Sales Contract:
- Confirming the sales contract and terms of transaction such as payment terms.
- Preparing Payment and Insurance:
- Preparing payments and insurance specified in sales contract (eg. when payment term is D/C, submit D/C application to the issuing bank; when trade term is FOB, arrange cover note with an insurance company).
- Preparing insurance, cover note, when necessary
- Acquiring Goods:
- Receiving shipping advice and arrival notice
- Receiving export documents from the exporter
- Collecting goods from the specified shipping company or forwarder
- Customs Clearance: Arranging customs clearance and import declaration
Import Procedure
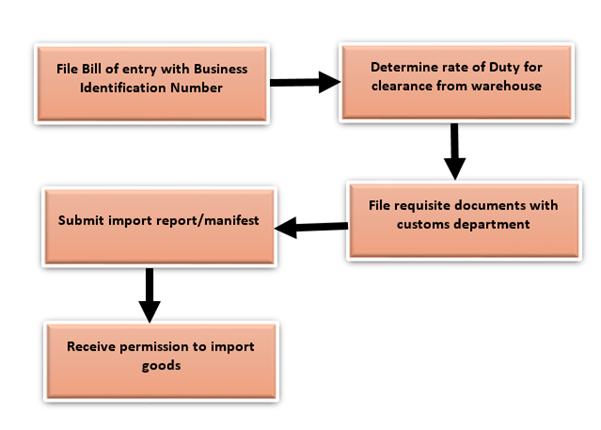
All importers must have to follow detailed customs clearance formalities when importing goods into India. A complete overview of EXIM procedures can be found on the Indian Directorate of General Valuation's website.
It is established in finance literature that smooth, efficient and compliance oriented exporting, importing needs specialized knowledge of personnel. In many companies some or all functions of export and import department are combined in some way. In smaller companies, where the volume of export and import does not justify more personnel one or two person may have responsibility for both export and import documentation and procedures. In giant companies, these functions tend to be separated into export department and import department (Johnson, 2010).
It is beneficial for companies to have export and import manual of procedures and documentation. These manuals serve as an effective tool for smooth operations and as a training tool for new employees. Exporters and importers must maintain record relating to their international trade transaction. Many companies offer software program for managing the export process such as order taking, generating of export documentations compliance with export control regulation, calculation of transportation charges and duties. On import side, many companies offer supply chain management software.

