Global Business Strategy
In international business, it is imperative to devise effectual Global Business Strategy in order to thrive in competitive world. An international feature of growth of global business has been the extent to which multinational corporations have developed commercial relationships intermediate between internalization of activities within their own organizational hierarchies. Management theorists explained global Business Strategy as the business strategies engaged by the businesses, companies or firms operating in a global business environment and serving customers at global scale.
Global business strategies are associated with the business developing strategies adopted by businesses to meet their short and long term objectives. The short term goals of the business would be related to enhance daily operations of the company whereas the long term objectives are generally directed towards increment of the profits, sales and earnings of the company in the long run ensuring development and strength of the business and supremacy over the national or local market. Global business strategies evolve due to globalization and internationalization of established national companies which is supposed to upsurge the value of the company.
In competitive platform and process of globalization, there is strong pressure on managers and academicians to reconsider the formulation of global business strategy. global business strategy differs from a national business development strategy because other factors such as product standardization and adaptation involve in global strategies It is established in literature that global business strategies rests on two prime factors of standardization and adaptation.
Standardization of production by companies who involve in global business entails producing the same product for the national as well as the international markets with minute changes in qualities. It has been emphasized by theorists that basic human needs are the same in all nations at global level. This strategy to expand the global business has been supported by personalities such as Levitt, Buzzell, Yip, Loewe and Yoshino. The notion of standardization first developed in the 1960's and reappeared in the 1980's and it has been adopted successfully by many Japanese and European organizations which have experienced higher levels of product and process innovations which in turn have represented as source of comparative advantage for these companies in the transnational market. Many theorists supported the global business strategy of standardization. These theorists stated that standardization benefits in the economies of scale accruing to the company with it being able to produce in huge quantities using more or less the same methods of production.
Standardization retains the image of the home country which houses the global corporation since it assists to decrease the costs of alteration, design or modification, handling and stocking the product, speeding up delivery systems. It also assists to save the managerial time and effort to take decisions regarding the manufacture of different products. Standardization helps in faster accumulation of the learning experience as fallout of the learning-by-doing approach.
To oppose the process of standardization, many challengers the strategy of market orientation using the techniques of adaptation or local adaptation argued that while basic human needs may be similar ubiquitously, standardization may not be effective as differences in cultural and other environmental factors considerably influence the buying pattern of people in different nations. This viewpoint was supported by Boddewyn, Soehl Picard, Douglas, Sommers and Kernan.
A global business strategy may be suitable in industries where firms face numerous challenges strong for cost reduction but with weak pressures for local responsiveness. Therefore, it allows these firms to sell a standardized product internationally. Managers who develop global strategy think in an integrated way about all aspects of a business-its suppliers, production sites, markets, and competition. It involves assessing every product or service from the viewpoint of both domestic and international market standards.
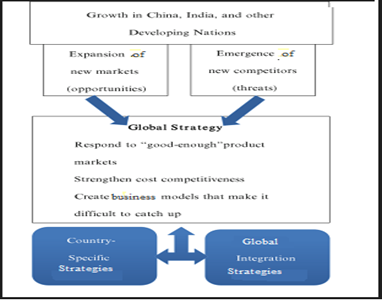
Global Business strategies are addressed by the interdisciplinary issues of marketing, organization theory, business strategy and international management and focuses to increase the firm performance. It depends on selecting a global strategy that is appropriate for the set of circumstances facing each business. Choosing an international strategy, be it standardization or adaptation is contingent upon the ability of the firm to suit its marketing strategy and the external environment. A theoretical contingency framework is often theorized between the critical variables of the business such as high sales revenue, capacity utilization and specific relationships between these variables and their operational implementation results in enhanced performance. For example Japanese companies shape their global business strategies considering the growth importance of developing nations in global economy. Important directions of global strategies are respond to good enough product market, strengthen cost competitiveness and create strong business models in which it is difficult to catch up (Kazuyuki Motohashi, 2015).
Global Business strategies for developing nation (Source: Kazuyuki Motohashi, 2015)
To summarize, global business strategies are devised by professionals to compete in the age of period of globalisation. It is important that companies must develop leaders that can operate throughout the world, lead global teams, and create operational strategies both globally and locally.

