Planning
Planning is the primary function of management. It is the important process of deciding business objectives and charting out the method to accomplish these goals. This includes decision of what type of activity is to be done, where to be done and how the results to be analyzed.
Theoretical review: Many theorists thoroughly describe the planning process of management function. Koontz and O'Donnel stated that "Planning is deciding in advance what to do, how to do it, when to do it and who is to do it. It bridges the gap from where we are and to where we want to go. It is an essence of the exercise of foresight. Another management theorist, M.S. Hardly explained "Planning is deciding in advance what is to be done". It involves the selection of objectives, policies, procedures and programs from among alternatives. Heying and Massie defined "It can be said that planning is first function of the manager in which he has to decide in advance action that is to be done." It is an intellectual process in which managers must have to use their imaginative mind. Planning is an attempt to foresee the future in order to get high performance.
Plans have numerous benefits. Planning enables managers to think ahead. It leads to development of performance standards. Plan forces management to articulate clear objectives. Planning makes organization to get ready for unexpected developments.
Planning includes various features such as Planning is mainly concerned with looking into future. In planning process, management team has to select suitable course of action under particular business environment. It means there are several ways to achieve objectives. Planning is done at all levels of the organization because managers at all levels are concerned with determination of future course of action. Planning is persistent and constant managerial function.
Nature of planning: planning is a rational approach, open system, flexibility and pervasiveness. It clarifies where one stands, where one wants to go in future and how accomplishes goal. Rationalist denotes a manager chooses suitable way to achieve the stated objectives and rational approach fills the gap between the current status and future status. Planning is an open System approach in which firm is an open system because it accepts inputs from the environment and exports output to environment. Planning accepts an open system approach. Open system approach designates that the gap between current and desired status and the action required overpassing this gap which is influenced by array of environmental economic, legal, political, technological, socio-cultural and competitive factors. These factors are vibrant and change with time. Therefore managers have to take into account the dynamic features of environment while using open system approach. Another aspect of planning is the flexibility of Planning: it means plan has ability to change direction to take on to changing situations without excessive cost. Many scholars said that the plans must be stretchy to become accustomed to changes in technology, market, finance, personal and organizational factors. However flexibility is possible only within limits, because it involves extra cost. Another feature is pervasiveness of Planning. Planning is persistent and it broadens throughout the organization. Planning is the primary management function and every manager at different level has to do planning within his particular area of activities. Top management is responsible for general objectives and action of the organization. Therefore it must plan what these objectives should be and how to achieve them. Similarly a departmental head has to develop the objectives of his department within the organizational objectives and also the methods to accomplish them.
Significance of Planning Process
Planning has core value in all organization whether business or non-business, private or public, small or large. The organization which has mindset for future is likely to succeed as compared to one which fails to do so. Planning establishes the objectives and all other functions are performed to achieve the objectives set by the planning process. The company constantly interacts with the external dynamic environment where there is high risk and ambiguity. In this changing dynamic environment where social and economic conditions change quickly, planning assists the manager to adjust with and prepare for altering environment. Through rational and fact based process for making decisions, manager can lessen market risk and uncertainty. Planning focuses on organizational objectives and course of action to accomplish targeted goal. It facilitates managers to apply and organize all resources of the organization successfully in achieving the objectives. The whole organization is required to embrace identical goals and work together in achieving them. Planning establishes the goal and develops plan to attain them. These goals and plans become the standards against which the actual performance can be measured. Control involves the dimension of actual performance, comparing it with the standards and taking remedial action if there is divergence. Control makes certain that the activity confirms to plans. Hence control can be exercised if there are plans. Planning also enhances organizational effectiveness.
Types of Planning
Planning can be categorized as coverage of activities, importance of contents in planning, approach adopted in planning process, time dimension and degree of formalization in planning process.
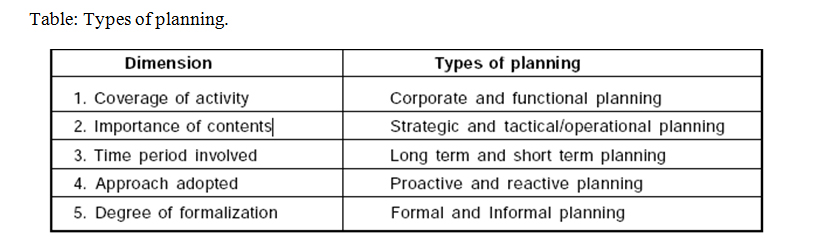
The planning activities at the corporate level which include activities of whole organizational are termed as corporate planning. Corporate planning is done to chase long term objectives as a whole and to create plans to accomplish these objectives bearing in mind the possible changes in dynamic environment.
Strategic planning sets future directions of the organization in which it wants to proceed in future such as diversification of business into new lines, planned growth rate in sales. It has three major characteristics such as it embraces all activities of organization, has long time horizon and successful implementation. Operational planning involves to decide effectual use of resources already allocated to achieve the organizational objectives such as adjustment of production within available capacity, increasing the efficiency of the operating activity by analyzing past performance. The long term planning is strategic in nature and involves more than one year period and can extend to 15 to 20 years. Proactive planning develops appropriate courses of action in expectation of likely changes of environment. Managers who adopt proactive changes do not wait for environment to change, but take action in advance of environmental changes. To get success, it is necessary to continuously review the environment conditions. In reactive planning, response comes after environmental changes occur. Informal planning is done by small organizations. This planning process is based on manager's experience, intuitions instead of methodical evaluation of environmental changes. This planning process is part of manager's normal activity.
Mainly two types of plans are formulated in management that includes standing plans and single use plans. Standing plans give guidelines for advance course of action and are used over a period of time. Standing plans are designed for situations that persist often enough to justify a standardize approach. Single use plans are intended for specific end when that end is reached, the plan is dissolved or devised again for next end.
Major Steps in Planning Process
The planning process is different from one plan to another and varies from company to company. Common steps in planning are mentioned below:
- Establishing goals or objectives: The initial phase of planning process is to establish the business objectives. These organizational goals are made by senior level managers after reviewing numerous objectives. These objectives are based on the number of factors like mission of the organization, abilities of the organization. Once management team establishes the organizational goals, the section wise or department wise objectives are planned at the lower level. Defining the objectives of every department is important and accordingly precise direction is given to the departments.
- Establishing planning premises: The next step in planning which involves establishing planning premises is the conditions under which planning activities will be done. Planning premises are planning statements that are the expected environmental factors, pertinent facts and information relating to the future such as general economic conditions, population trends, and competitive behavior. The planning premises can be Internal and External premises, Tangible and Intangible premises, Controllable and non-controllable premises.
- Deciding the planning period: After determining the long term objectives and planning premises, another phase is to choose the period of the plan. Some plans are made for a year and other plans are devised for longer period. There are many factors which influence the choice of a period. Lead time in development and commercialization of a new product. Big companies like an aircraft building company plans for a period of five to ten years where as a small manufacturer can commercialize his idea in a year. Another factor is time needed for recovery of capital investment or the payback period. The payback period also influence the planning period. Length of commitment already made also impact the choice of time span in planning. Researchers emphasized that the plan period should be made in such a way that it can fulfil the commitments already made. Identification of alternatives is important factor in determining time frame in planning. A particular objective can be achieved through various actions. Evaluation and selection of alternative is the next step which assess the alternatives with the support of the premises and goals and to choose the best course or courses of action.
- Developing derivative/supportive plans: After selection process of plan done, various plans are derived so as to support the main plan. These derivative plans are devised from the main plan.
- Measuring and controlling the process: It is advised that plans once established should not be executed unless its progress is monitored. Managers must have continually monitor progress of their plans so that remedial action can be taken to make fruitful plan.
Obstacles in planning Process
It is observed that many executives involve in implementing plans instead of spending time to develop effectively. It is founds that there are many barriers that inhibit planning process. In order for plans to be effective and to get the desired results, managers must recognize any potential barriers and make efforts to reduce them. Common barriers that hinder successful planning are as under:
The first barrier is incapability to plan or it can be said as inadequate planning. Managers do not have inherent quality to devise effective plan. Some managers are not successful planners because they do not have ability, education to develop planning for particular situation. Such incapability creates hindrance in planning process.
Another barrier is lack of commitment to the planning process. Planning process require hard work. Another cause for lack of commitment can be fear of failure. As a result, managers may choose to do little or nothing to help in the planning process.
Inferior information also creates hindrance in planning process. It is observed that poor information or of inadequate quantity can be major barriers to planning. Even though managers are proficient in planning but if they do not have latest information their plans will possibly fail.
Another barrier to planning process is failure to consider the long‐term effects of a plan because more emphasis is given to short term issues. This may result in preparing for the future.
If managers excessively depend on the organization's planning department, their plans may not be successful. Many companies have a planning department or a planning and development team. These departments conduct studies, do research, build models, and project probable results, but they do not implement plans.
In order to make effective plan, keep the planning process simple. It is advised to discuss the objectives of organization with top level team before preparing for plans and use participative approach in developing plan.
It can be concluded that management planning is the process to evaluate an organization's goals and create a realistic, detailed plan of action for meeting those goals. Planning is the continuous process of systematically making plans with the knowledge of the future, organizing the activities needed to carry out the plans and monitoring the results of the plans through comments. Planers must communicate plan to other staff members as why specific action is taken.

