Product Strategy (Marketing Management)
In marketing expressions, a product is any object or service which is made available in a market to satisfy a want or need of customers. A product can be a physical object or a service and may refer to a single item or unit, a group of comparable products or a group of goods or services. Most business marketing managers devise an understandable and practical product strategy prior to the launch of a new product into its future market.
Products have three constituents that include:Core product: This is the end benefit for the purchaser.
Formal product: This is the actual physical or apparent characteristics of product including its level of quality, special features, styling, branding and packaging.
Augmented Product: This level is about discovering if there are any added non-tangible benefits company can offer. Competition at this level is based around after sales service, warranties, and deliveries and so on.
Philip Kotler in his book "Principles of Marketing" formulated significant concept of benefit building with a product.
Figure: product should be viewed on three levels.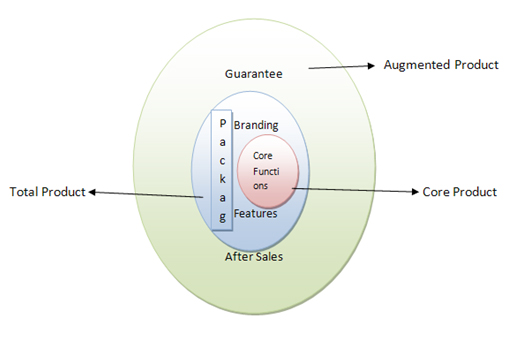
When product is created, a company's product strategy is based upon its business strategy. Product strategy starts with a planned vision of where a company wants to go, how it will get there, why it will thrive.
Many factors and decisions have to be taken into consideration when placing a product within a market.

The whole product: The whole product link the gap between the marketing promise companies makes to clients and its product's ability to deliver on that promise. It includes all the products and services that are necessary to augment or complete the product so that it becomes a complete solution and lives up to its value proposition.
Common principles of product strategy:product strategy must describe the vision of company that try to accomplish. Another principle is that the product strategy is the bridge between the business strategy and the product roadmap and coming up with a good product strategy.
The four layers of the whole product
Generic product: The product that is shipped after a purchase.
Expected product: The product the purchaser believes he buys when he orders the generic product.
Augmented product: The idealized form of the product that gives the greatest chance that the customer will accomplish his fixed buying purpose.
Potential product: The noticeable growth path of the benefits demonstrated by the product as it is improved, and as it is complemented and strengthened by other products and services. The concept of the whole product represents a functional means for start-ups. It gives benefits for product development and planning. It assists the decision-making process for partnering, distribution, and customer service and buyer motivation.
It is stated that Business Company who wants to introduce some product into the stream of commerce must plan and design a product strategy cautiously. Two major product strategies include price-based product strategy and product differentiation. When utilizing price-Based Product Strategy, the product is designed according to factors like cost-plus pricing, value-based pricing, and target-return pricing. Fundamentally, strategic viewpoint in a price-based strategy is to put the price in such a way that new product has a competitive advantage over other similar products. In order to execute a price-based product strategy, it is necessary to consider price discounts. After choosing a price-based method, and after formulating strategy, company managers will arrive at a list price. Discounting the price lowers the list price, but makes purchasing the product more profitable. Product Differentiation strategy is used when company and competing firms offer a product that fulfils the same need. In a product-differentiation strategy, major objective is to put distance between product and competitor's product. There are two forms of product differentiation, vertical differentiation and horizontal differentiation. To execute a vertical product-differentiation strategy, main goal is to improve quality of product so that the customers observe a difference in quality. Horizontal differentiation focuses on customers' preferences and should be used when the features of product cannot differ substantially from the features of competitors.
When developing new product development strategy, it is important to consider following factors:
Define your product: A precise description of the product that are planning will help keep company and management team focused and avoid product development pitfalls such as developing too many products at once, or running out of resources to develop the product.
Identify market needs: Successful product development requires a systematic knowledge of company's target market and its needs and wants. A targeted, strategic and purposeful approach to NPD will ensure products fit targeted market. It is necessary to consider that nature of the target market for proposing the product, market need, benefit of proposed new product, and the market's issues of existing products of its type, how will the product fit into the current market and what sets this product apart from its competition. It is essential to describe existing market research. Companies may need to start additional research to test new product proposal with focused consumers.
Another important factor in developing new product strategy is to establish time frames. Organizations need to allocate sufficient time to develop and implement new products. Company's objectives for developing new products will inform time frames and deadlines for implementation. Company must aim to attain a specific launch date that will be influenced by demand for seasonal products and calendar events. Organizations must aim to be receptive to customers' needs and demands that will require time for research to ensure it to develop the right products at the right time.
Identify key issues and approaches: There are many tasks involved in developing a product that is appropriate for customers. The nature of business and idea will decide how many of these steps need to take. Major tasks include generating and screening ideas, developing and screening concepts, testing concepts, analysing market and business strategy, developing and market testing products and implementing and commercialising products.
To summarize, Product Strategy is the most significant function of a company. Companies that have good product strategy can perform better over extended periods of time than companies that implement multiple technologies and/or seek market diversity.

