Quality Management
The quality concept today is vital part of business at a global level. The quality management system is intended to improve productivity and enhance customer satisfaction. The quality management system promotes companies to evaluate hidden needs of consumers, identify the processes that develop quality products which are according the expectations of shopper, and control business process. Quality management is the basis for business achievement of any firm. The concept of quality has huge importance in business management literature since 1950 when scholars concentrated on this issue.
The concept of quality in business focuses on the savings and additional profits that organizations can realize if they remove mistakes throughout their operations and produce products and services at the best level of quality desired by their customers. American Society for Quality defined that quality is based on customer's perceptions of a product/service's design and how well the design matches the original specifications, and the ability of a product/service to satisfy stated or implied needs and it is achieved by conforming to established requirements within an organization. The ISO definition of quality is that quality is conformance to requirement, the totality of features of the product that bear on its ability to satisfy stated and implied need (Suganthi, 2004). The development of quality management is strongly related to the automobile industry, as many quality approaches were applied early on in the automobile sector and brought a common enhancement to both worlds. Toyota pioneered many quality principles, such as the origins of Total Quality Management (TQM), Just-In-Time Management, or Lean Management, and Ford can be seen as prime example for the effect of quality principles on business performance. Theoretical studies described that a quality management system is a management method used to communicate to workers what is required to produce the desired quality of products and services and to influence employee actions to complete tasks according to the quality specifications. Factors that represent need of customers include utility value, affordable cost, longer life, reliable performance, product look, ease of maintenance and prompt after sale service (Suganthi, 2004).
Purpose of quality management: The main objective of the quality control in firms is that management must take initiatives to provide products that have better customer value and improve organizational outputs. The belief of Quality management is to guarantee quality in products and services offered by organization. Quality Management System has major aim to establish a vision for the employees, set standards for employees, build motivation within the company, sets goals for employees, help fight the resistance to change within organizations and assist to direct the corporate culture.
Quality improvement is required to achieve business success. It may simply be the extent to which organization can produce superior-quality product or service than competitors are able to do at a competitive price. When quality is the key to a company's success, quality management systems allow organizations to sustain with and meet current quality levels, meet the consumer's requirement for quality, hold employees through competitive reward programs, and continue with the newest technology.
Historical review of quality management: In the decade of the 1950s, Japanese companies started realizing the benefits of emphasizing quality throughout their organizations and enlisted the help of an American, W. Edwards Deming, who is accredited with giving Japanese companies a huge start in the quality movement. His methods include statistical process control (SPC) and problem-solving techniques that were very successful to gain the necessary impetus to change the attitude of organizations needing to produce high quality products and services.
Quality experts of 20th century like Crosby, Deming and Juran broadly elucidated the quality of products in two categories. The first category is the quality of product that satisfies applicable specifications. Quality is a simple matter of producing goods and delivering services whose measurable characteristics meet the fixed set of specifications that usually are numerically defined. Other one is quality that satisfies the consumer. Independent of any measurable characteristics, quality products is simply those that satisfy customer expectations for their use or consumption (Nanda, 2005). Fundamentally, quality management includes all activities that are required to plan for quality in an organization and satisfy quality objectives.
Activities of Quality Management (Nanda Vivek, 2005)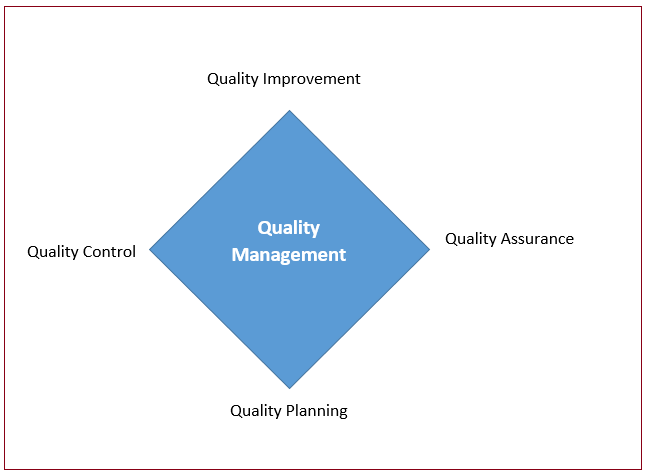
Deming is renowned as expert of total quality management. In his viewpoint, a shift to quality paradigm in a company is a transition towards a more mature management style (Nanda, 2005). Deming principle of quality management states that a product or service possesses quality if it helps somebody and enjoys a good and sustainable market.
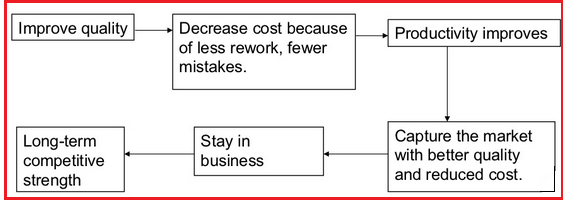
Deming philosophy of quality management is a set of fourteen principles (Table: 1). He developed the sequence reaction that means to improve quality, reduce costs and enhance productivity. This led to increase in market share, and long-term endurance of organization in marketplace.
Table: 1Deming's Fourteen Points for Management:
- Create constancy of purpose for improvement of product and services
- Adopt the new philosophy
- Cease dependence on mass inspection
- End the practice of awarding business on price tag alone
- Constantly and forever improve the systems of production and services
- Institute modern methods of training on the job
- Institute modern methods of supervision and leadership
- Drive out fear
- Break down barriers between departments
- Eliminate numerical goals for the work force
- Eliminate work standards and numerical quotas
- Remove barriers to pride of workmanship
- Institute a vigorous programme of education and training for everyone
- Create a structure in top management that will push every day on the above 13 points
The main belief of the quality control in companies is that management team should work hard to develop goods and services that have good value for purchaser and it can augment organizational production. The principle of Quality management is to make certain quality in products and services presented by global companies. Gitlow et al. represented that quality is the declaration that ushers a product or service delivered according to customer standards, devoted to fulfil the demands of the purchaser, meets expectation of the buyer and also satisfies unexpected needs in the future (1989). Plentiful management studies of the quality management have disclosed that company must continually track on quality of products and services offered for gratification to customer and fulfil their needs. Gitlow et al. indicated that quality is the assurance which escorts a product or service delivered according to customer standards, committed to fulfil the needs of the customer, meets expectation of the customer and also satisfies unexpected needs in the future 1989.
Abundant studies of the quality management demonstrated that it is important for firm to continuous track on quality of products and services offered for real satisfaction to customer and meet their needs. On the other hand, Foley, et. Al. argued that "Continuous improvement of quality of service and/or product cannot be the end to which competitive business is directed. Whilst every business wants to remain viable then continuous improvement and customer satisfaction can only be a means to an end and not an end in itself. There may be times in the life of an enterprise where, to satisfy its survival (profit) criterion, it will be necessary to discontinue or slow down the rate of quality improvement activity, however clear it might be that those activities would increase quality of product and/or service and customer satisfaction" (1987).
Philip Crosby theory of quality management states that quality is free. He believed that quality means getting it the right the first time rather than merely laying down acceptable levels of quality. Crosby initiated the zero defect program. There are fourteen steps of quality improvement declared by Crosby (Suganthi, 2004).
- Management of Commitment: First and primary, management must be committed to improving the quality in a company. This commitment must also be transparent to all employees so that proper attitudes towards a Zero Defect product or service line are modelled. This can be achieved by issuing corporate policy on quality need. Quality should be made first item on the agenda of the regular meeting.
- Formulate the Quality Improvement Team: Developing a quality improvement team is the next step to gain total quality management. Search for team members who will model quality improvement commitment and who are not already over-committed to other projects. The quality improvement team should be able to efficiently commit themselves to improvement of quality.
- Measurement for Quality in Current Practices: Before company can establish a plan for improving quality, they first have to know exactly where products and services lie when it comes to conforming to requirements. Thus, it is imperative to measure quality. Determine where there is scope for improvement and where potential for improvement exists.
- Cost of Quality: Quality is measured by cost of quality which is described as the expense of non-conformance that is the cost of doing things wrong.
- Quality Awareness: Company executives must need to raise employee awareness to the importance of quality management. In this way, and making quality a central concern to employees, they will increase the chance that their quality improvement efforts will be realized. It can be said that awareness must be adapted in culture of company. People must know the cost of doing wrong.
- Corrective Action: After assessing company's quality problems, it is now time to take corrective action to eliminate the defects that have been identified. Company must install a system, using causal analysis techniques, to ensure that these problems don't reoccur in the future. The main purpose of corrective action is to identify and eliminate problems forever.
- Zero Defects planning: executives need to create a committee to ensure that there are zero defects in their products and services. For Crosby, it's not enough, remember to have "as few as possible" defects. Instead, company really need to have this number at zero, establish a zero-defect tolerance in company. Zero Defects commitment represent major step forward in the thrust and longevity of quality management process. It must be taken seriously and planned in very dignified way.
- Employee education: Company must develop complete education system that would provide standard message and could be taught by anyone who trained to us. It must be ensured that supervisors can carry out the tasks required of them for maintaining quality. By practicing supervisor training, with quality in mind, they will be more likely to achieve zero-defect status.
- Zero Defects Day: It is a day to get management to stand up and make its commitment in front of everybody. It is a time to hold a quality event, called a zero defects day, where all employees are made aware of the change that has taken place. By holding a zero defects day in company when implementing a total quality management project, it can be sure that officials are increasing awareness for quality in workplace.
- Goal Setting: Goal setting is something that happens just after measurement. This must be chosen by the group as much as possible and should be put up on a chart so that everyone can see. By bringing everyone in the company on setting goals for improvement, you can ensure greater commitment to achieve zero defects.
- Eliminate Causes of Errors: This is asking people to state their problem so that something can be done about them. Error-cause removal is required for the successful implementation of any quality improvement effort. It is necessary to encourage your employees to come to management with any obstacles or issues that arise in meeting improvement goals. By having employees communicate obstacles before they become crises, company can avoid many of the dampers for quality improvement efforts.
- Recognition for Participants: It is the implementation of employee recognition. Award programs must be established to recognize those who meet the goals of outstanding act. By regularly recognizing those who participate in quality improvement efforts, employees will be much more likely to continue to participate.
- Generate Quality Councils: By bringing together specialists and employees, executives of company can create a focused effort towards creating lasting quality improvement implementations. Make sure quality councils meet on a regular basis.
- Do it all over again: Quality improvement does not end. In order to really make improvements in the quality of products and services, Company will need to do it over again and again. Always ready to get started on quality improvement projects.
Another famous theorist of quality control was Joseph M. Juran, who, focused on improving quality. Juran also established the Juran Institute in 1979 and its goals and objectives were to assist organizations to improve the quality of their products and services. Juran defined quality as "fitness for use," meaning that the users of products or services should be able to rely on that product or service hundred percent of the time without any worry of defects. Juran also developed a wide-ranging approach to quality that covered a product or service's entire life cycle, from design to customer relations and all the steps in between. Juran advocated that an organization should scrutinize all processes and procedures from a quality viewpoint and investigate for a "fitness for use." Once this is completed the organization can start to make changes based on the "fitness for use" model. Juran's ten steps of quality improvement are as follows:
- Build awareness of need and opportunity for improvement: Realize that all processes are improvable.
- Set goals for improvement: Juran's formula for results is, establish specific goals to be reached. Establish plans for reaching the goals. Assign clear responsibility for meeting the goals. Base the rewards on results achieved.
- Organize to accomplish goals; Such as establish quality council, identify problems, select projects, appoint teams, and designate facilitators.
- Provide training: Training is important for quality improvement.
- Carry out projects to solve problems: Large improvements are usually the result of interdepartmental or even cross-functional quality improvement teams. These teams tackle the constant problems that have been in the way of company progress for a long time.
- Report progress: Necessary actions to improve the status can be initiated to reduce the variance. Information on the progress also provides the management the confidence on the Improvement activity and further support if required.
- Give recognition: Recognition is a means to provide morale to both those involved in the improvement activity and all others in an organization. This is a vital activity to be done by the management as improvements provide a change for betterment resulting in savings to the company and at times, the improvements are made possible against lot of criticisms.
- Communicate result: Lesson learnt during the improvement process requires to be shared to create an awareness of the approach taken and the possibility to learn and improve further.
- Keep score: A Company's goals are achieved step-by-step.
- Maintain momentum by making annual improvement part of the regular process of the company:
Other theorist who explained the concept of quality management was Clause Moller. He developed the principle of personal quality as main element of total quality management. He explained 12 rules to quality improvement (Suganthi, 2004).
- Set personal quality goals
- Establish own personal quality account.
- Check how to satisfy others with your efforts.
- Regard the next link as a valued customer.
- Avoid errors.
- Perform task more efficiently.
- Utilize resources well.
- Be Committed.
- Learn to finish what you start.
- Control your stress.
- Be ethical.
- Demand quality.
Quality must be integrated into the design process by moving its focus to early stages of the production life cycle, thus eradicating the need for mass inspections. This means operational cost reduction when shifting from a reactive to a proactive mode. Deming highlights the need for quality management to build quality into the product. "Quality at the Source" denotes that every single employee is responsible for quality in every moment. Devoted quality departments should be made redundant by this quality approach, since they are decoupled most of the time from internal matters of the production process and will never be as efficient in determining insufficiency.
Numerous quality management programs which are used to enhance product and services are Six Sigma, Theory of Constraints and Total Quality Management. Six Sigma is a practical management concept and problem-solving procedure but it is not a complete management system. TQM is a management approach in which quality is highlighted in every aspect of the business and organization. Major goal of TQM is long-term development of quality products and services. TQM breaks down every process or activity and emphasizes that each contributes or detracts from the quality and productivity of the organization as a whole. The important characteristics of total quality management are that it includes all organization, and suppliers and customers. Tobin affirmed that TQM is incorporated program to gain competitive advantage through continuous improvement in organizational environment (1990). Management's role in TQM is to increase a quality scheme that is flexible enough to be adapted to every department, aligned with the organizational business objectives, and based on customer and stakeholder needs. Once the strategy is defined, it must be the motivating force to be deployed and communicated for it to be successful at all levels of the organization.
Principles of Quality Management
- Customer Focus: This standard is associated with customer needs and customer service. Business should understand their customers and try to find ways to fulfil their requirements. Where possible, they should aim to surpass customer expectations. In this way, company can increase customer loyalty, increase revenue due to the ability to find new customer opportunities and increase effectiveness of processes related to customer satisfaction.
- Leadership: This standard is linked with the direction of the organisation. Company's business should have clear objectives and workers should be actively involved to accomplish these goals. It will assist company to enhance motivation of employee engagement. Numerous researches have shown that if employees are involved in making to business vision they are likely to be more prolific.
- Involvement of people: This principle identifies that company staff has great significance and that their abilities should be used for business success. This will enable company to enhance employee enthusiasm and increase innovation.
- Process Approach: The process approach relates to efficiency and the understanding that appropriate processes will speed up activities.
- System approach to management: ISO define that identifying, understanding and managing interrelated processes as a system, contributes to the organisation's effectiveness and efficiency in achieving its objectives. This means that manifold processes are managed together as a system which should lead to greater efficiency. This allows a business to focus their efforts on the processes for success as well as supporting complementary processes for improved efficiency.
- Continual improvement: Continual improvement should be an active business objective. It will increase ability to hold new opportunities, organisational flexibility and improved performance.
- Realistic approach to decision making: A logical approach, based on data and analysis, is good business sense. Informed decisions lead to improved understanding of the marketplace as data is collated and analysed, and the ability to defend past decisions.
- Mutually beneficial supplier relations: This standard relates to supply chains and acknowledges that the relationship between an organisation and its suppliers is interdependent. A strong relationship between the two will augment productivity and encourage seamless working practices.
Benefits of Quality Management
Quality management has numerous advantages. At international level, many industries, service organizations, and educational institutes have implemented quality system. These organizations get many advantages such as reduction in complaints from customers both internal and external, decrease in cost of the product, reduction in cost of production time, increased system efficiency, increased morale of workman, increased customer satisfaction.
Benefits of quality system (Source: Suganthi, 2004 )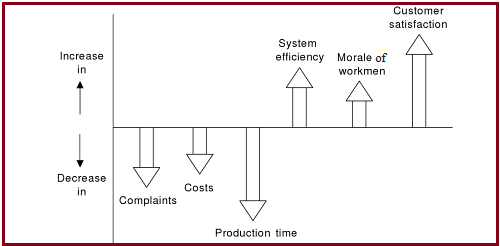
In present business scenario, criteria of quality have been changed. Companies and customers both look differently the product quality.
Table: changing views on quality (Source: Suganthi, 2004 )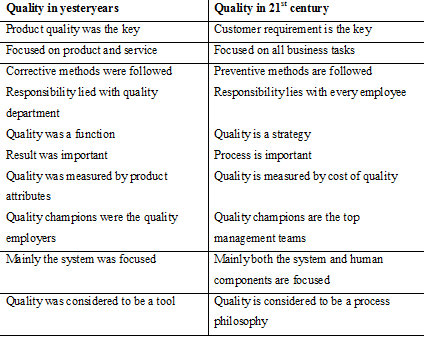
ISO 9001 Quality Management: ISO stands for the International Organisation for Standardisation which consists of the national standards bodies of 91 nations. Its main role is to develop international standards to improve the exchange of goods and services internationally. The ISO 9001 standard is a quality management standard. ISO 9001 Management Systems can assist in decreasing costs by tracking and measuring outputs and identifying areas of waste or repetition. It has numerous advantages such as it offers improved product or service quality and consistency so customers know what they are getting time and time again. The ISO 9001 certificate is suitable for all types of firms and educational corporations and is well recognized at international level as a valuable quality management system.
To summarize, quality management assist an organization to grow up in market place. Companies execute different procedures and instructions to develop and transport products as per the anticipations of customers. Quality management enhances quality by involving processes, environment and people over the period of time to fulfil the requirement of respected customers. Organizations are involved in continuous quality improvement to thrive in the international open market. Many studies established that organizations are dependent on their customers and apply array of method to enhance quality in order to satisfy potential customer needs. Companies can achieve target through offering better quality product or service in today's competitive market. Quality management program helps Company to maintain current quality levels, assure the consumer's demands for quality and sustain the latest technology.

