Services and Non Profit Marketing
Marketing process is highly important for the triumph of any company. There are numerous marketing practices adopted by marketer to gain competitive advantage. In marketing area, in global economy, there is more importance service sector. This is mainly due to the growing significance and share of the service area in the economies of most urbanized and developing countries. Actually, the development of the service sector has been considered as indicative of a country’s monetary growth. Service is an intangible product that includes a deed, performance, or an effort that cannot be actually possessed. Main constituent is intangible. It includes rental of goods, modification and repair of goods owned by clientele, and personal services. Many service firms stress technical expertise, therefore have lagged in their use of marketing. Many service firms are small therefore marketing expertise cannot be hired. According to The American Marketing Association, services are activities, benefits and satisfactions which are offered for sale or are provided in connection with the sale of goods. Basically, services is an activity or series of activities taken place by interaction between customers and service employees. Famous theories, Kotler described services as an activity or benefit that one party can offer to another that is essentially benefit that one party can offer to another that is essentially intangible and does not result is the ownership of anything. Its intangible and does not result is the ownership of anything. Its production may or may not be tied to a physical product.
The life of services marketing has undergone three stages:
- The Crawling Out stage (Pre-1980)
- The Scurrying About stage (1980-1985)
- The Walking Erect stage (1986-today)
The Crawling Out Stage (Pre-1980) is a period of high risk. The objective was to prove the right of services marketing to exist.
The Scurrying about Stage (1980-1985): Main characteristics include noteworthy increase in the interest of practitioners and academics in the case of services marketing, the debate on the uniqueness of services marketing was partly won. The objectives were to reinforce, even further, the argument that, despite similarities, the marketing of services necessitated a different management approach. Outcomes in this period were significant growth of the empirically based knowledge on the special nature of services such as Service quality, Service encounters, Service design and new service development.
The Walking Erect Stage (1986-2003): In this period, the objective was to conduct empirical research in new areas of inquiry in services marketing. The empirical orientation and rigorousness of research on services marketing increased. New areas of inquiry are empirically investigated such as Customer retention, Relationship marketing, Green issues in services marketing, Branding services, Internationalisation of services, Direct services marketing, Sponsorship in services, and Franchising in services.
Features of a service are:
Intangibility: Services are intangible and do not have a physical existence. Hence services cannot be touched, held, tasted or smelt. This is most important characteristic of a service and that which mainly differentiates it from merchandise. Also, it creates a unique challenge to those engaged in marketing a service as they need to attach tangible feature to an otherwise intangible offering.
Heterogeneity/Variability: Each service offering is unique and cannot be exactly repetitive even by the same service provider. While products can be mass produced and be homogenous the same is not true of services.
Perishability: This is the peculiar quality of services as these cannot be stored, saved, returned or resold once they have been used. Once rendered to a client the service is completely consumed and cannot be delivered to another customer.
Inseparability: This feature of services denote to the fact that services are generated and consumed within the same time frame. Furthermore, it is very complicated to separate a service from the service provider.
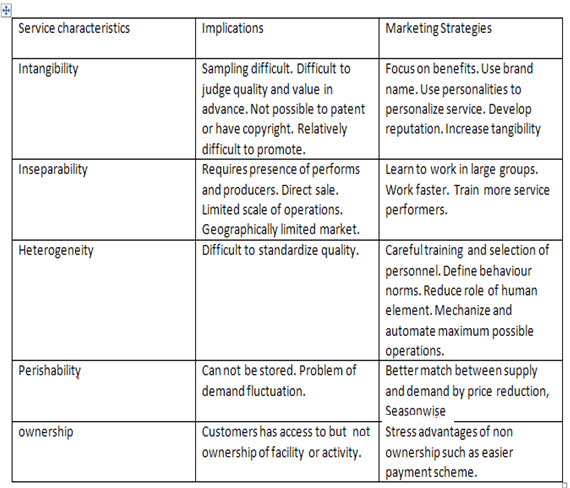
society it serves Implications of service characteristics and ways to overcome (R. Srinivasan, 2004)
Implications of service characteristics and ways to overcome (R. Srinivasan, 2004)
Theoretical framework demonstrated that Services marketing is one of the major subdivision of marketing, which can be divided into the two main areas of goods marketing and services marketing. Services marketing usually refer to both business to consumer and business to business services, and include marketing of services like telecommunications services, monetary services, hospitality services, health care services and professional services.
Service marketing mix: The Service Marketing Mix entails Product, Price, Place, Promotion, People, Process and Physical Evidence. Firms marketing a service need to get each of these elements accurate. The marketing mix for a service has added elements because the features of a service are different to the characteristics of goods. To certain extent, managing services are more difficult as compared to management of products because products can be standardised but it is complex to standardise a service as there it can be affected by factors outside the service providers’ control.
Product: With reference to services, the ‘product’ is intangible, heterogeneous and perishable. Moreover, its production and consumption are inseparable. Hence, there is scope for customizing the offering as per customer requirements and the actual customer encounter therefore assumes particular significance. However, too much customisation would compromise the standard delivery of the service and adversely affect its quality. Therefore, special care has to be taken in designing the service offering.
Pricing: Pricing of services is more difficult than pricing of goods. Price is a vital tool in marketing of service. Since it is often difficult to assess a service before purchase, price acts as a marker of perceived quality. It also play dominant role in managing demand.
Below three elements of service marketing mix which are unique to service marketing:
People: People are an essential element in service provision; recruiting and training the right staff is required to gain competitive advantage. Customers make judgments about service provision and delivery based on the people representing any organisation. This is because people are one of the few elements of the service that customers can see and interact with.
Process: This component of the marketing mix evaluates at the systems used to deliver the service. An efficient service that replaces old credit cards will foster consumer loyalty and confidence in the company. All services need to be underpinned by clearly defined and competent processes. This will avoid uncertainty and encourage a consistent service.
Physical Evidence: Physical evidence is the environment where the service is being delivered from. It is predominantly applicable to retailers operating out of shops. This component of the marketing mix will discriminate a firm from its competitors. Physical evidence includes the services scape, a term used to describe the physical facility where the services is produced or delivered. Physical evidence can be used to charge a best price for a service and establish a positive experience. Physical evidence is the constituent of the service mix which allows the customer again to make judgments on the organization. Consumers will make perceptions based on their sight of the service provision which will have an impact on the organizations perceptual plan of the service.
Services marketing mix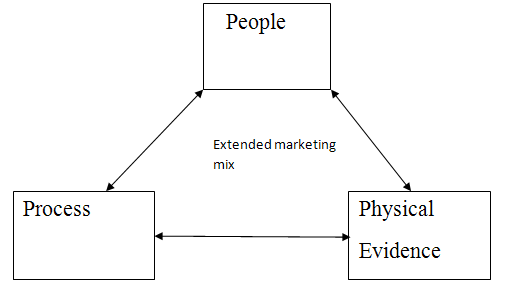
E-Service marketing: Internet technology is major driver of growth of service economy. E-service is electronic service available via net. This service can be used by people, business and e-services.
Illustration of e-services: (R. Srinivasan, 2004)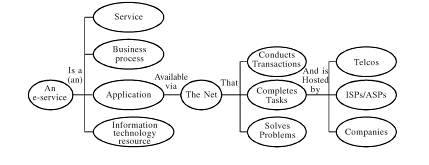
To summarize, Service marketing is emerged as fastest growing sectors in modern economy. It is becoming a marketing view point which is beneficial not only to service firms but also for any situation where consumption cannot be characterized as process consumption. Service marketing fact is driven by scholars of marketing as they are influenced by varying nature of economic environment and need of management.
Non Profit Marketing
Non Profit Marketing has distinct place and its effective approach is beneficial for society. This type of marketing is associated with activities and policies adopted by a non-profit organization that are intended to spread the message of the organization, and to request donations and call for unpaid assistants. Non-profit marketing engages in the formation of logos, slogans and copy, as well as the development of a media campaign to depict the organization to outside addressees. It is found that in non-profit organizations, various marketing approaches are used to enhance the image and reputation of the organization in culture and assist the public to remember the organization and its cause. Marketing policies help to distinguish one non-profit from another non-profit that is offering similar programs. Marketing tactics are used to attract and hold donors and volunteers. According to Philip Kotler, “Marketing is the function of a non-profit whose aim is to plan, price, promote, and distribute the organization’s programs and products by keeping in constant touch with the organization’s various constituencies, uncovering their needs and expectations for the organization and themselves, and building a program of communication to not only express the organization’s purpose and goals, but also their mutually beneficial want-satisfying products.”
Non-profits marketing are described as the effectual use of marketing schemes to further the goals and objectives of non-profits organizations. There are numerous examples of non-profit organization tactics such as advertising, public relations, and fund-raising. Non-profit marketing also includes wide range of other activities. Gathering and processing information for decision making are considered as vital element of non-profit marketing. Relations with governments, board members, donors, and volunteers are part of non-profit marketing. Non-profit Marketing is performed by companies and individuals that work in the public interest or that promote a cause and do not look for financial gain. Management theorists stated that a non-profit organization is an organization that utilizes its grant to chase a specific purpose, such as a charitable cause, instead of getting profits. Non-profits use marketing approaches to aid with growth, financial support and prosperity.
Non-profit Marketing does exchanges but not necessarily financial. Price is not essentially an indication of the costs or values. A nonprofit organization can move towards in marketing in similar way as a for profit business. It should recognize its target market, develop marketing materials to send to that target market, and establish the objectives that a marketing crusade should meet. It has been observed that the nonprofit organization follows the four P's of marketing: product, place, price and promotion. It is vital for the non-profit to develop its brand’s image. The brand is normally a logo, wording, motto or design that recognizes the group. The look and content of all communication, events, service, leadership, coalitions and the organization’s office expresses the brand of the non-profit. The experiences that clients have with the nonprofit organization also lead to the overall brand of the organization. The brand allows donors, supporters and customers to consider, recognize and trust the organization. It keeps the nonprofit organization detach from similar organizations by building an individuality.
Dimensions of Nonprofit Marketing: There are various dimensions of nonprofit marketing such as planning, positioning, communicating, and attracting resources.
Planning: Marketing experts in nonprofit organizations, or nonprofit marketers, devise plans to assist the nonprofit organizations to accomplish its strategic goals.
Positioning: Nonprofit organizations generally benefit from being broadly acknowledged in society. There are numerous nonprofit organizations and many opportunities for people to contribute to a praiseworthy cause. A non-profit’s first job in competing for donations is becoming renowned to the society it serves. Persons attached to these organizations actively communicate commercial marketing messages throughout the day. Once the nonprofit organization is known, another job is to persuade the public’s perception of the organization.
Positioning task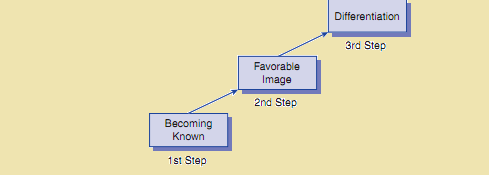
Communication: Communication is vital marketing activity that facilitates the organization to accomplish its marketing goals. The nonprofit organizations direct its communications to its various stakeholders. Stakeholders are groups that have more interest in the nonprofit organization. Generally, these include the organization’s customers, board members, employees, volunteers, donors, granting organizations, government, other non-profits, and the communities served by the nonprofit organizations. A non-profit’s customers are the people to whom it provides services. There must be effectual communication for the exchange between consumer and organization to be triumphant. Board members must be recruited and engaged. Employees require to recognize the goals and objectives of nonprofit organizations. They need to have an influence in the development of plans. Volunteers must be employed and retained. Donors must be acquired and appreciated. Non-profits often communicate with government officials to represent their causes and interests. The communities served by a nonprofit must understand about its services. Victorious nonprofit organizations establish relationships with their stakeholders and develop relationships with them. Non-profits’ communication programs are a main resource to approach and maintain contact with stakeholders.
Resource Attraction: Nonprofit marketers have significant resource attraction function. Donations of time denotes to the staffing and preservation of volunteers. Donations of funds entail contributions from organizations and individuals. These contributions can be in-kind donations, such as products company manufacturers, or monetary donations.
Resource Attraction Function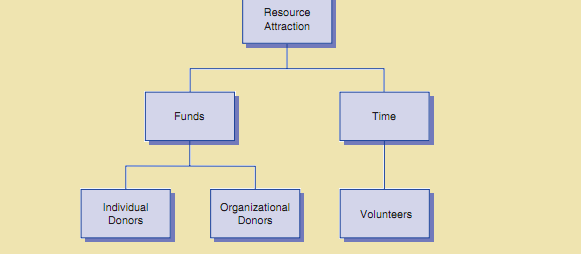
Major factors in Nonprofit Marketing: There are many factors needed to keep in mind in implementing non-profit marketing.
Branding: Branding is highly important for nonprofit managers. Nonprofit managers consider a non-profit’s brand as its image or reputation. It is the way the organization is perceived by the community. Powerful, positive brand provides advantages for the nonprofit. The most broadly known organizations have greater reliability because people already be acquainted with about the organization and its work. Non-profits are generally known for big team of potential donors. Through positioning activities, a nonprofit helps the public to understand its purpose and how it differs from other non-profits and how the nonprofit is extraordinary. Through consistent public relations communications to various audiences, non-profits establish favourable reputations.
Social Marketing: Social marketing is described as the use of marketing approaches in the establishment, implementation, and control of programs considered to influence social change. Several non-profits need to enhance public health or social conditions. To accomplish this mission, they must explore ways to boost public wakefulness of an issue and assist a people or a subgroup of society change to a more healthful set of behaviours. Changing human behaviour is difficult, even when the change is useful.
Use of the Internet: Non-profits organizations utilize the Internet. Websites are used to converse with external groups. A proficiently designed website reflects the professionalism of the nonprofit. Non-profits also raise funds online. They employ volunteers online. E-newsletters and e-mails are sent to supporters. Online surveys obtain marketing information. Educational materials are distributed online. Products are sold online.
Nonprofit organizations undergo several challenges that including shrinking budgets, donor fatigue, a proliferation of competing organizations, and increased donor scepticism. In broad sense, nonprofit marketing is a management orientation that assists the nonprofit organization expand its sphere beyond its internal operations and programs to also include the external world that affects the organization. A nonprofit organization that has a marketing orientation concentrates on its different activities and external communications to project a consistent image of itself and persuade the way the external world perceives it.

