Six Sigma
The notion of Six Sigma is really imperative in business arena it eliminates mistakes and errors and thus attains perfection. Six Sigma is an advance tool in quality management and process improvement since last two decades. Six Sigma is recognized in various types of organizations since the 1990s. Most Fortune 500 companies have accepted Six Sigma (Goh, 2002). Reports have showed that Six Sigma can assist firms to accomplish significant performance enhancement. The phrase 'Six Sigma' is emerged from the statistical foundation of the methodology (Das et al., 2008). Some Scholars consider that Six Sigma is merely a repackaging of the well-known total quality management program. It measures how far a given process deviates from perfection. It is associated with 'process capability', a process that operates at six sigma will produce no more than 3.4 defective parts per million although this will debase over time to around a 99.5% yield. Most companies will operate at around 1 to 2. Six Sigma is well-organized process that helps to focus on developing and delivering near-perfect products and services. Six Sigma invented at Motorola in the beginning of 1980s, in response to achieve 10X decrease in product-failure levels in 5 years (Barney, 2002). Engineer Bill Smith discovered Six Sigma. The Six Sigma is based on numerous theories of quality management (Deming's 14 point for management, Juran's 10 steps on achieving quality). The main scheme behind Six Sigma is that if one can measure how many "defects" have in a process, then it can systematically figure out how to eliminate them and get as close to "zero defects" as possible and specially it means a failure rate of 3.4 parts per million or 99.9997% perfect.
Motorola got the success through implementing Six Sigma. Subsequently, Six Sigma was promoted to many Fortune 500 companies in the decade of 1990 where it also assisted them to accomplish desired outcomes. Popular companies such as AlliedSignal, currently known as Honeywell, GE, and 3M adopted the process of Six Sigma. At the same time, Six Sigma also went through significant development. Mainly, GE improved Six Sigma through new practices. Later on, GE asserted that Six Sigma has become a vital part of its business culture and strategy (Barney, 2002). GE's success further extended Six Sigma to small and medium sized businesses. After two decades from its evolution, Six Sigma is not only a defect rate measure but it has a statistics core, a precise improvement method, and an exclusive practices (Breyfogle et al., 2001). Six Sigma is a wide-ranging system to realize, sustain and maximize business success of companies (Ranawat et al, 2007). This system facilitates companies to understand customer needs, to use facts, data and statistical analysis more disciplined, and to manage, improve and explore business processes (Pande, Neuman, Cavanagh, ,2000).
While Six Sigma has usually been related with manufacturing and product quality but currently, it has been applied to many other industries and services. Top manufacturers are using it to improve their Logistics capabilities (Ranawat et al, 2007). Six Sigma has been incorporated into culture. Logistics companies optimise the processes while decreasing variations and improving the expansion of supply chain and other development of sectors. Additionally, it has been recognized that the accurate application and use of Six Sigma can considerably cut out excess cost by 50%, improve time cycle, and minimize the waste of materials, increase customer happiness, and cuts millions of miles from delivery routes from their supply chains.
Six Sigma is considered as an improvement approach or an improvement program. According to Schroeder et al. (2008, p. 540), Six Sigma is an organized, parallel-meso structure to reduce variation in organizational processes by using improvement specialists, a structured method, and performance metrics with the aim of achieving strategic objectives. It is a methodology to develop the products and processes that perform at high standard. It is a quality philosophy and management technique.
Reflecting its manufacturing background, Six Sigma is often attached with the Lean Manufacturing methodology, creating amalgam known as Lean Six Sigma. Lean compliments Six Sigma by adding a focus on process flow and waste elimination. An additional difference is that of Design for Six Sigma (DFSS). While Six Sigma is used to enhance the performance of existing processes, DFSS is used to design high performance directly into new processes or products.
Many business and quality development professional avowed that Six Sigma is the most popular management methodology in history. Six Sigma is now a huge 'brand' in the arena of corporate development. Though this methodology began in 1986 as a statistically-based method to decrease variation in electronic manufacturing processes in Motorola Inc in the USA, presently, Six Sigma is used as a grand business performance method, around the world, in organizations as diverse as local government departments, prisons, hospitals, the armed forces, banks, and multi-nationals corporations. While Six Sigma execution continues rapidly in many of the world's major corporations, many organizations and suppliers in the consulting and training communities have also apprehended on the Six Sigma theory, to wrap up and provide all sorts of Six Sigma 'branded' training products and consultancy and services. The original and technically correct spelling seems to be Six Sigma, rather than 6 Sigma, although in recent years Motorola and GE have each since developed their own sexy Six Sigma logos using the number six and the Greek sigma characters.
Key Concepts of Six Sigma
Six Sigma revolves around a few key concepts.
Critical to Quality: Attributes most important to the customer.
Defect: Failing to deliver what the customer wants.
Process Capability: What process can deliver.
Variation: What the customer sees and feels.
Stable Operations: Ensuring consistent, predictable processes to improve what the customer sees and feels.
Design for Six Sigma: Designing to meet customer needs and process capability.
Features of Six Sigma
Major aim of Six Sigma is to eliminate waste and wastefulness, thus increasing customer satisfaction by delivering what the customer is expecting.
Six Sigma follows a structured methodology, and has definite roles for the participants.
Six Sigma is a data driven method, and requires precise data collection for the processes being analysed.
Six Sigma is about putting results on Financial Statements.
Six Sigma is a business-driven, multi-dimensional structured approach for:
- It is an improving Process.
- It is used to lower Defects.
- It reduces process variability
- It also reduces costs
- Application of Six Sigma enhances customer satisfaction
- Its use increases profits
Calculation of Six Sigma
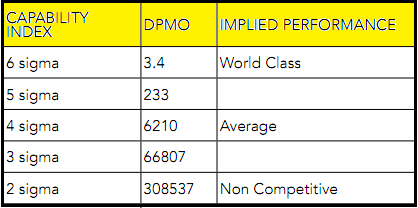
The model of Six Sigma is helpful to eliminate defects/variations in processes with respect to customer requirement. Achieving a six-sigma level quality means that processes produce only 3.4 defects per million opportunities (DPMO). Six-Sigma in addition to being a methodology for improving process capability is also viewed as a philosophy that leads to faultlessness on a continuous basis. The capability index, DPMO and the implied performance at select levels are mentioned below:
Design for Six Sigma (DFSS) Examine what Design for Six Sigma is and its importance, Understand why DFSS is important to Six Sigma implementation, Understand robust design and functional requirements, Develop a robust design using noise strategies and understand the concepts of tolerance design and statistical tolerance. It calculates tolerances using process capability data.
Methodology of Six Sigma: There are three methodology of six sigma:
- Business process management system (BPMS)
- DMAIC (Six Sigma improvement methodology)
- DMADOV (Creating new processes which will perform @ Six Sigma)
Six Sigma can also be applied within DMAIC and DMADV models.
DMAIC: It is most popular process improvement methodology which consists of Define, Measure, Analysis, Improve and Control. DMAIC is recognized as a simple performance improvement model that is used within an intense use of statistical computer software, and is acronym for Define-Measure-Analyse-Improve-Control. The DMAIC process can be described as following:
- Define the goals of the improvement activity
- Measure the existing system
- Analyse the system
- Improve the system
- Control the new system
It is a quality tool with focus on change.

Briefly, DMAIC is used by improving an existing process or service to attain the company's goal or the project objective. DMADV model is short form for "Define-Measure-Analyse-Design-Verify" where it focuses in Design and Verify stages.
The six sigma DMAIC model (Source: Gaspersz, 2007)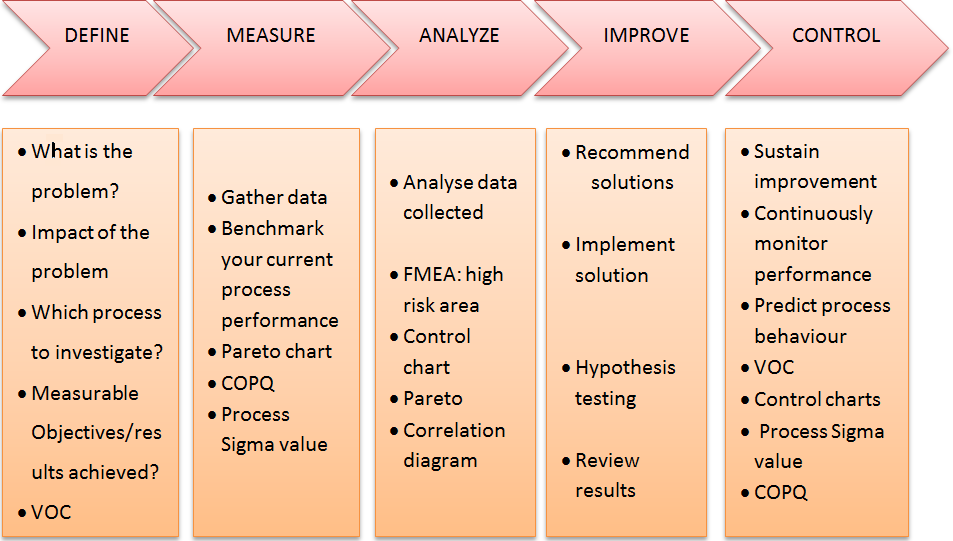
DMADOV comprises of define, measure, analyse, design, optimise and validate. DMADOV forces attention on the need to optimise the design (Kubiak,, 2009). This six sigma model is used to develop new processes and product at high quality level or if a process that is already in the company needs more than just an incremental improvement (Baird, 2009).
Benefits of Six Sigma
Six Sigma has numerous benefits that attract companies:
It generates sustained success
It sets a performance goal for everyone
It enhances value to customers
It speeds up the rate of improvement
It promotes learning and cross-pollination
It executes strategic change
Disadvantages of Six Sigma: Six Sigma is applied to all aspects of the production and planning process, it may create inflexibility and bureaucracy that can create delays and stifle creativity. In addition, its customer focus may be taken to extremes, where internal quality-control measures that make sense for a company are not taken because of the overlying goal of achieving the Six Sigma-stipulated level of consumer satisfaction. For example, an inexpensive measure that carries a risk of a slightly higher defect rate may be rejected in favour of a more expensive measure that helps to achieve Six Sigma, but adversely affects profitability.
To summarize, Six Sigma has been influential tool for the quality enhancement in today's competitive business world and gives the potential to improve current approaches to logistics improvement. It reduces waste, as well as it also offers benefits by delivering reduced variations. As result, good outcome of Six Sigma implementation will drive the increase in customer satisfaction, increase in profits, decrease in cycle times and higher flexibility (Ranawat et al, 2007). Six Sigma as an improvement mechanism is developed by Motorola in1985 that covers a set of strategies and tools acquired in order to improve the current business practice and methodical processes to fulfil the objectives. It is originally designed to measure faults or defects in the process so that they can be eliminated systematically as part of improvement to reduce flaws and enhance quality. Initially Six Sigma was first integrated into manufacturing industries. This methodology also applies well to logistics companies since the focus is customer-oriented. Supply chain management is a main strategic factor for increasing organizational efficiency and for better realization of goals such as enhanced competitiveness, better customer care and increased profitability (Gunasekaran, Patel, Tirtiroglu, 2001). Consequently, Six Sigma is considered to be successful method in delivering business benefits through variant reduction.

