World Class Manufacturing
With the initiation of industrial insurgence, manufacturing has emerged globally. In competitive business environment companies must improve their manufacturing practice which is lean, efficient, lucrative and flexible. World class manufacturing is a group of concepts, which develops standards for production and manufacturing for another organization to follow. Japanese manufacturing is attributed for revolving the notion of world-class manufacturing. World class manufacturing was introduced in many sectors like automobile, electronic and steel industry. The objectives of World-Class Manufacturing efforts are to maintain market share, improving profitability and improving the firm's ability to compete in a global market place (Montgomery et al 1996).
World Class Manufacturing was originally used by Hayes and Wheelwright in 1984 to explicate companies that gained international competence by utilizing manufacturing skills. They explained world class manufacturing as a set of practices, implying that the use of best practices in order to enhance performance. They mentioned numerous critical practices, such as development of the workforce, developing a technically competent management group, competing through quality, stimulating worker participation and investing in state of-the art equipment and facilities. Schönberger elaborated the principles of World Class Manufacturing and gave many examples. His main concentration was on continuous improvement, development of supplier relationships, product design and JIT to the practices cited by Hayes and Wheelwright. Schonberger offered a list of 16 principles of WCM which were grouped into eight categories such as general, design, operations, human resources, quality and process improvement, information for operations and control, capacity, promotion and marketing. Schonberger told managers to appraise their own plants based on these 16 principles (1986). In common language, a world class producer is powerful to flourish at global business market. Farsijani and Carruthers (1996) presented a model which demonstrated the growth of techniques and factors related with the belief of WCM. This model is an advanced toolbox from 1980 onwards, with respect to the industrial environment and organizational requirement. However, the model of Farsijani and Carruthers (1996) had some limits, it lacks distinct structure and cataloguing for its techniques.
To achieve huge success in business at international level, on the basis of World Class Manufacturing principles, companies must adopt precise manufacturing strategies. The correct manufacturing approach deliver on the shortest lead time, always on time, offer a product with good features as compare to competitors, made perfectly, to meet the expectations of the customer, can produce in quantities as required and at lowest cost.
Manufacturing Excellence and WCM
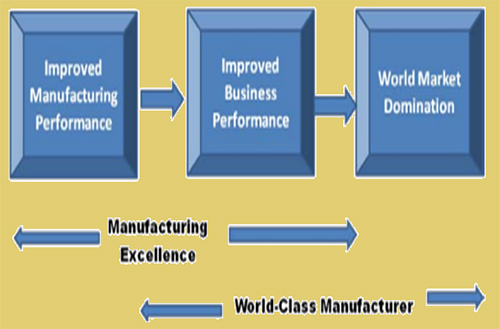
World class manufacturing has been characterised by three core strategies of customer focus, quality, and agility such as the ability to quickly, efficiently and effectively respond to change and six supporting competencies; employee involvement (EI), supply management, technology, product development, environmental responsibility and employee safety (Kinni, 1996). It is necessary for organizations to consider some critical factors that may impact implementation process and address them effectually to guarantee benefits and evade failures when executing World Class Manufacturing concept. These factors are management commitment, quality department, continuous improvement and customer involvement. Theorist, Greene defined that "WCM companies are those companies which continuously outperform the industry's global best practices and which know intimately their customers and suppliers, know their competitors' performance capabilities and know their own strengths and weaknesses. All of which form a basis of continually changing competitive strategies and performance objectives (1991, p. 14). The perception of World Class Manufacturing is in reality in the manufacturing set up which can be implemented through the proper tools and methods such as Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) and within it Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), SMED, pull and kanban system, continuous flow, visual management, team work, JIT, 5S, waste elimination, Statistical Process Control (SPC), Zero Quality Control (parts per million – PPM).
Figure: Factors of World Class Manufacturing
The Implementation of World Class Manufacturing
Management studies denotes that any organization can get success if it provides soothing conditions for improvement of both manufacturing and administrative processes. The implementation of world class manufacturing is usually organized in the companies by separate department whose job is to train employees about how to use WCM notion and methods, then organisation of individual projects, all that recording in the documentation, and evaluation of results and their distribution. World class manufacturing department addresses and aligns three major areas that include People, Process and Production:
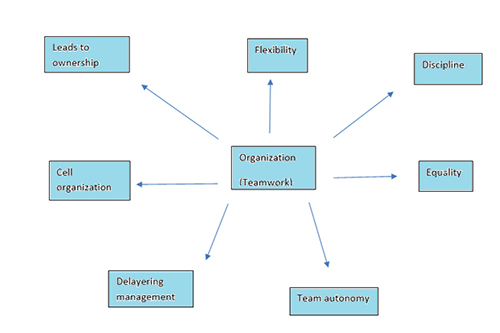
- Area: People: Teams and peoples in the company work in secure atmosphere to accomplish goals of management and to satisfy the customer needs. Company must give more emphasis on health, safety, environmental thinking and behaviour. Management considers an education and training of people, then leading people to teamwork.
- Area: Processes: the process is a series of individual actions performed in a specific sequence that create value. It is important that processes must be standardized and give superior results over time and that the maintenance of processes and equipment must proceed well.
- Area: Production: Flow is the rhythmic and continuous transmission of the right material and precise information within the manufacturing operations at the correct time, in the right quantity and in the right way. The objective of flow production is to decrease product throughput time and human energy through a series of appropriate actions. The role of World Class Manufacturing engineer is to
- Implement and communicate the World Class Manufacturing concept in a company and oversight its proper implementation.
- To train top management and other company managers in World Class Manufacturing practices and assist them in implementing their training sessions.
- Introduce indicators, collect and visualize the results achieved by the company.
- Find solutions in World Class Manufacturing area of how to optimize resources for individual company departments;
- Find solutions to the demands of workplaces regarding World Class Manufacturing methods.
- Collaborate in defining company strategy in terms of World Class Manufacturing activities.
- Prepare meetings with company management.
- Introduce methodological procedures.
- Plan the necessary financial and human resources in the implementation of World Class Manufacturing.
Obstacle to World Class Manufacturing Implementation:
It is well established in management studies that World Class Manufacturing is a necessary practise for the achievement of competitiveness. It combines a system of knowledge, techniques, experiences, skills, and organisational characteristics that are needed to produce, utilise and control output. World Class Manufacturing is critical to competition, because the techniques and resources it combines can create new opportunities. Such an approach is given added motivation by speedy technological changes and aggressive competition, requiring manufacturers to consider the adaptation of recent techniques of World Class Manufacturing. Nonetheless, many theorists have argued that WCM implementation has a number of limitations that must be addressed in the manufacturing strategy (Hollensen, 2001). When executing the World Class Manufacturing techniques, there are many barriers such as partial implementation of WCM techniques, optimistic expectations and implementation of WCM to conform to societal norms rather than for its instrumentality (Campbell, 1994). Major problems in World Class Manufacturing application include incomplete implementation, lack of a well-defined routine for attaining the objectives of implementation, cultural resistance to change, lack of training and education, and lack of organizational communication (Crawford et al., 1988). Safayeni et al. (1991) stated that ineffectiveness of WCM implementation is due to misperception over what exactly constitutes World Class Manufacturing and its implementation within an existing organization structure that does not provide the necessary support. The main obstacle that affect World Class Manufacturing implementation is the incapability of a company to synchronize its human resource practices, management policies and technology (Fredendall et al., 1997).
To sum up, world-class manufacturing is a manufacturing management viewpoint that focuses on constant enhancement of manufacturing practises through human resource development. Management must put more emphasis on higher standards of quality, flexibility, and productivity. It represents a blend of various concepts, principles, policies and techniques for the management and operation of companies engaged in production.

